Alpha Centauri (α Cen) is a triple star system located in the southern constellation of Centaurus. It is the nearest star system to the Sun and the third brightest point of light in the sky outside the solar system, after Sirius and Canopus. It outshines the northern luminaries Arcturus, Vega and Capella. With a combined apparent magnitude of -0.27, Alpha Centauri is also the brightest point of light in Centaurus, visibly outshining its neighbour Hadar (Beta Centauri) and the orange giant Menkent (Theta Centauri).
The Alpha Centauri star system consists of three components: Rigil Kentaurus (Alpha Centauri A), Toliman (Alpha Centauri B), and Proxima Centauri (Alpha Centauri C). Proxima Centauri, the faintest component, is the nearest individual star to the Sun, located only 4.2465 light years from Earth. The brighter Rigil Kentaurus and Toliman lie at a distance of 4.344 light years. They form the Alpha Centauri AB binary system, which appears as a single star to the unaided eye.
Proxima Centauri hosts the nearest planetary system to Earth. Three exoplanets have been detected orbiting the star to date. Two are confirmed and one is disputed. Proxima Centauri b, an Earth-sized planet discovered in 2016, orbits in the star’s habitable zone.
A candidate planet orbiting Rigil Kentaurus, named Candidate 1 (C1), was directly imaged by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and reported in 2025, but has yet to be confirmed. Two candidates have been detected orbiting Toliman, but neither has been confirmed.
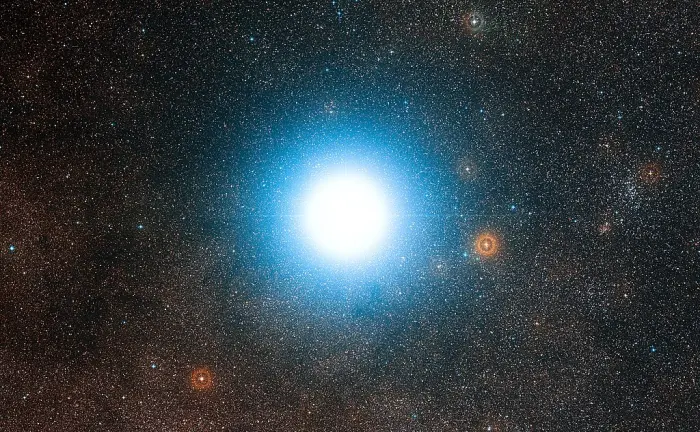

This wide-field view of the sky around the bright star Alpha Centauri was created from photographic images forming part of the Digitized Sky Survey 2. The star appears so big just because of the scattering of light by the telescope’s optics as well as in the photographic emulsion. Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to the Solar System. Image credit: ESO/DSS 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Star system
The Alpha Centauri system consists of Alpha Centauri A, a yellow main sequence star of the spectral type G2V, Alpha Centauri B, an orange main sequence star with the stellar classification K1V, and Alpha Centauri C, a faint red dwarf of the spectral type M5.5Ve.
The components Alpha Centauri A and B, formally named Rigil Kentaurus and Toliman, form the binary star system Alpha Centauri AB. The two stars appear as a single star to the unaided eye but can be easily resolved in smaller instruments. Their total mass is about 2 solar masses. With an absolute magnitude of +4.38, Alpha Centauri A is more luminous than Alpha Centauri B (+5.71).
The two Sun-like stars are locked in a 79.762-year orbit with an eccentricity of 0.51947 ± 0.00015. Their orbit takes them within 11.2 astronomical units of each other and as far apart as 35.6 astronomical units. Their most recent closest approach (periastron) occurred in August 1955 and the next one will be in 2075.
In 2019, the angular separation between the two stars was 4.92 arcseconds and it increased to 5.49 arcseconds in 2020. The observed apparent separation between the stars has been in the range from 1.7 arcseconds to 22 arcseconds. The maximum separation (apastron) was observed in 1976. The next apastron will be in January 2056.
Since the eye can only resolve stars that are 60 or more arcseconds apart, the AB binary always appears as a single star. Most of the time, it can be resolved in binoculars and small telescopes.
Proxima Centauri orbits the main pair with a period of about 547,000 years (543,000 – 553,600 years) and an eccentricity of 0.50. While orbiting, it comes within 4,300 astronomical units (3,400 – 5,400 AU) of the main pair and gets as far away as 13,000 astronomical units (12,900 – 13,300 AU). Currently, the physical distance between the main pair and Proxima is about 0.21 light years, or 13,000 astronomical units. This is about 5% of the distance between the Sun and Alpha Centauri AB.
With an apparent magnitude of 11.11, Proxima is invisible to the unaided eye and does not appear in the immediate vicinity of Alpha Centauri AB. The red dwarf star lies 2.18 degrees southwest of the bright AB binary.
The Alpha Centauri star system is believed to be slightly older than the Sun. Estimates based on standard stellar models have yielded an age of 5.4 billion years for Alpha Centauri AB, while those based on asteroseismic observations and stellar parameters have yielded values of 4.85 ± 0.5, 5.0 ± 0.5, 5.2 ± 1.9, 6.4, and 6.52 ± 0.3 billion years. Gyrochronological methods have given an estimated age of 5.0 ± 0.3 billion years, and methods based on the stars’ chromospheric activity have yielded a value of 4.4 ± 2.1 billion years.
The value of 5.26 billion years for Alpha Centauri AB comes from a 2018 study led by M. Joyce of the Department of Physics and Astronomy, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH. The team used stellar models to fit to the classical and seismic observations of both components.
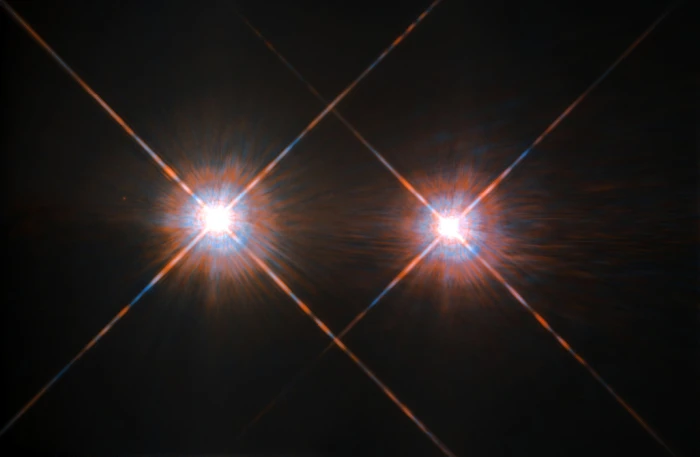

The closest star system to the Earth is the famous Alpha Centauri group. Located in the constellation of Centaurus (The Centaur), at a distance of 4.3 light-years, this system is made up of the binary formed by the stars Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B, plus the faint red dwarf Alpha Centauri C, also known as Proxima Centauri. The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has given us this stunning view of the bright Alpha Centauri A (on the left) and Alpha Centauri B (on the right), flashing like huge cosmic headlamps in the dark. The image was captured by the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2). WFPC2 was Hubble’s most used instrument for the first 13 years of the space telescope’s life, being replaced in 2009 by WFC3 during Servicing Mission 4. This portrait of Alpha Centauri was produced by observations carried out at optical and near-infrared wavelengths. Compared to the Sun, Alpha Centauri A is of the same stellar type G2, and slightly bigger, while Alpha Centauri B, a K1-type star, is slightly smaller. They orbit a common centre of gravity once every 80 years, with a minimum distance of about 11 times the distance between the Earth and the Sun. Because these two stars are, together with their sibling Proxima Centauri, the closest to Earth, they are among the best studied by astronomers. And they are also among the prime targets in the hunt for habitable exoplanets. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA (CC BY 4.0)
Rigil Kentaurus – Alpha Centauri A
Rigil Kentaurus, the primary component in the system, is slightly larger and more massive than the Sun. Like the Sun, it is a main sequence star of the spectral type G2V and it exhibits coronal variability due to star spots coupled with the effect of rotation.
The star has a mass 1.0788 times that of the Sun and a radius 1.2175 times solar. With an effective temperature of 5,804 K, it is 1.5059 times more luminous than the Sun.
Rigil Kentaurus has an apparent magnitude of +0.01. Individually, it is the fourth brightest star in the night sky, slightly outshining Vega (mag. +0.026), but fainter than Sirius (-1.46), Canopus (-0.74), and Arcturus (mag. -0.05).
Various catalogues give slightly different values for the star’s apparent magnitude. The Bright Star Catalogue and the Hipparchos and Tycho Catalogues (1997) list a visual magnitude of -0.01, while the Tycho-2 Catalogue gives a magnitude of +0.137, and the 2007 Hipparchos (the New Reduction) lists a value of +0.1373.
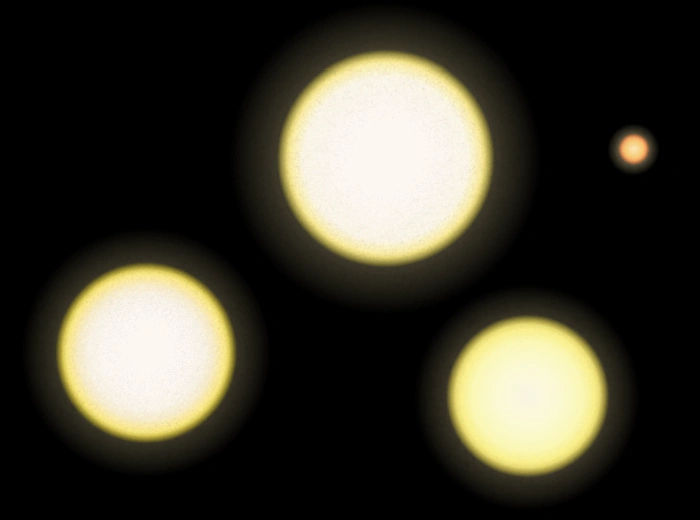

This diagram illustrates, from left to right, the relative size of the Sun, α Centauri A, α Centauri B and Proxima Centauri. Image credit: Wikimedia Commons/RJHall (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Toliman – Alpha Centauri B
Toliman is cooler, smaller and less massive than Rigil Kentaurus. With the stellar classification of K1V, it appears more orange in colour. The star has a mass of 0.9092 solar masses and a radius of 0.8591 solar radii. With a surface temperature of 5,207 K, it shines with only 0.4981% of the Sun’s luminosity. Like Rigil Kentaurus, it is about 5.26 billion years old, considerably older than the Sun.
Even though it is not as luminous as Rigil Kentaurus, Toliman has a greater energy output in the X-ray band and dominates the system’s X-ray emission. A flare was discovered on the star in 2005.
Toliman has an apparent magnitude of +1.33. As a single star, it would be the third brightest star in Centaurus, fainter than Rigil Kentaurus and Hadar (mag. +0.61), but outshining Menkent (mag. +2.06). By itself, the orange star would still be one of the brightest (first-magnitude) stars in the sky, slightly dimmer than Deneb (mag. +1.25) in Cygnus and Mimosa (mag. +1.25) in Crux, but brighter than Regulus (mag. +1.36) in Leo, Adhara (mag. +1.50) in Canis Major, and Castor (mag. +1.58) in Gemini.
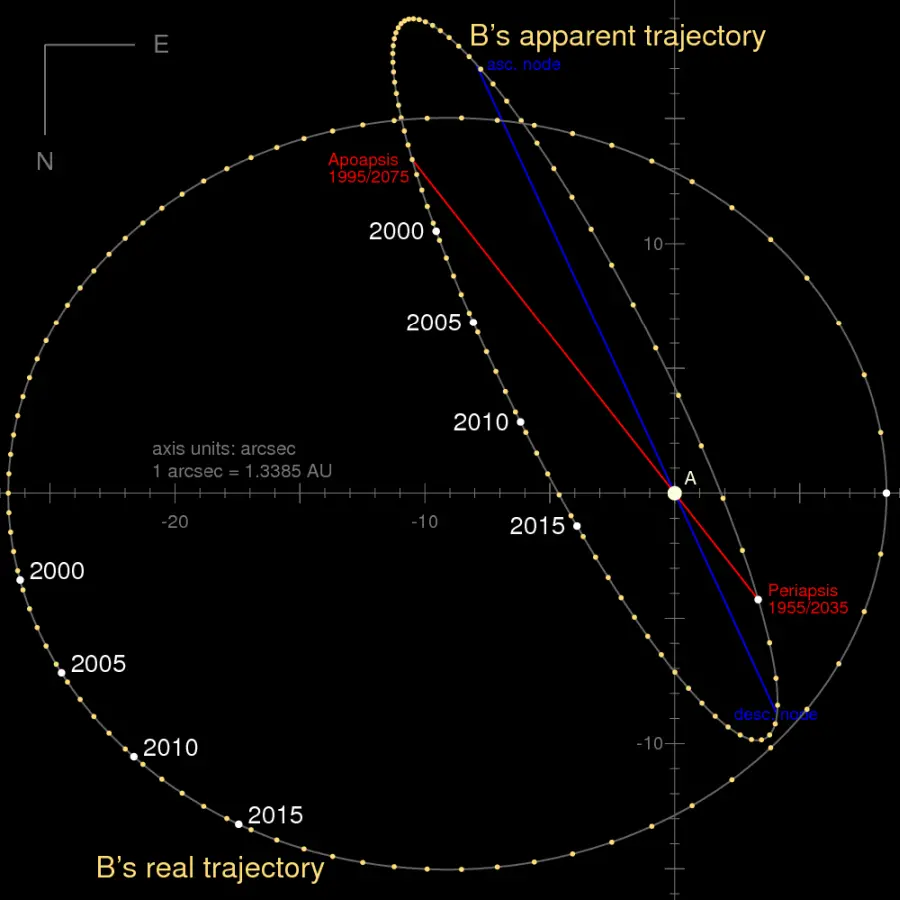
Trajectory of Alpha Centauri B relative to A (fixed to the coordinate origin) as seen from the Earth (inclined ellipse) and face-on (horizontal ellipse). The orbit parameters are taken from Pourbaix et al. (2002). Image credit: Wikimedia Commons/SiriusB (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Proxima Centauri – Alpha Centauri C
Proxima Centauri is the smallest of the three stars in the Alpha Centauri system. It is a red dwarf of the spectral type M5.5Ve. It has a mass of only 0.1221 solar masses and a radius of 0.1542 solar radii. With an effective temperature of around 2,992 K, the dwarf star shines with only 0.001567 solar luminosities. It is more than 20,000 times fainter than the Sun, with an absolute magnitude of +15.60.
With a visual magnitude that varies between 10.43 and 11.11, Proxima is very faint. Even from the Alpha Centauri AB system, it would only appear as a fifth magnitude star.
The star is classified as a UV Ceti variable, a flare star that shows sudden increases in brightness that last only for a few minutes. The increases in Proxima‘s brightness, up to magnitude 10.43, are caused by magnetic activity. The nearby red dwarf Wolf 359 also belongs to this group of variables. The prototype UV Ceti, also catalogued as Luyten 726-8B, is a red dwarf only 8.770 light years away. It is the most dramatic example of this type of star. Its brightness has been observed to brighten by 75 times within only 20 seconds. The largest observed flares of Proxima occurred on August 13, 2015, when the star’s brightness increased 8.3 times in the B band.
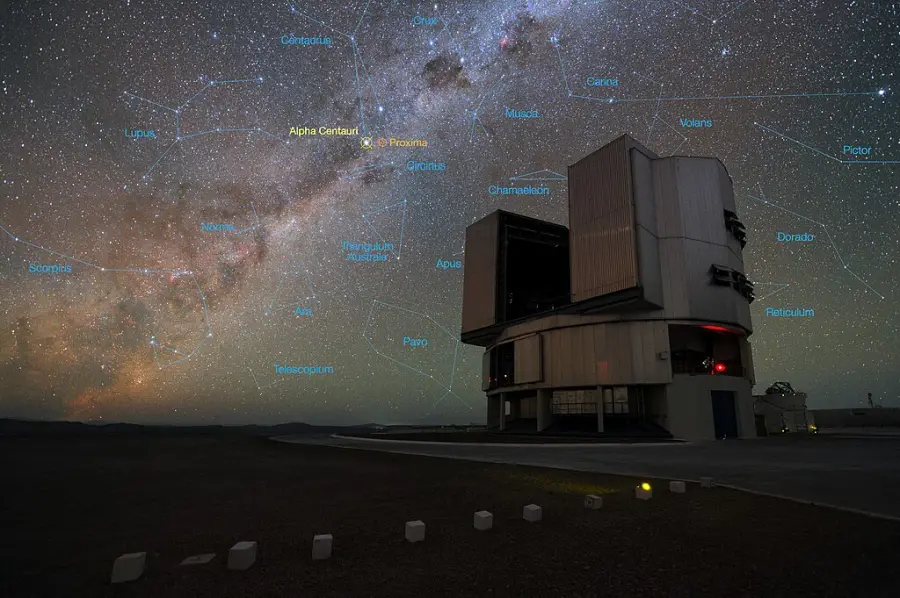

The foreground of this image shows ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) at the Paranal Observatory in Chile. The rich stellar backdrop to the picture includes the bright star Alpha Centauri, the closest stellar system to Earth. In late 2016 ESO signed an agreement with the Breakthrough Initiatives to adapt the VLT instrumentation to conduct a search for planets in the Alpha Centauri system. Such planets could be the targets for an eventual launch of miniature space probes by the Breakthrough Starshot Initiative. Image credit: Y. Beletsky (LCO)/ESO (CC BY 4.0)
Distance
The distance of Alpha Centauri AB is now believed to be 4.344 ± 0.002 light-years, or about 41.1 trillion kilometres, with a parallax of 750.81 ± 0.38 milliarcseconds. Proxima Centauri is slightly closer, at 4.2465 ± 0.0003 light-years.
Distance estimates for Alpha Centauri AB have varied somewhat over the last two centuries. In 1839, the Scottish astronomer Thomas Henderson calculated a distance of 2.57 ± 0.53 light years from a parallax of 1160 ± 110 milliarcseconds (mas). In 1842, he corrected the estimate to 3.34 ± 0.5 light years based on a parallax of 912.8 ± 64 mas.
In 1851, South African astronomer Thomas Maclear gave similar numbers – a distance of 3.55 light years with a parallax of 918.7 ± 34 mas. In 1868, German astronomer Karl Wilhelm Moesta calculated a distance of 3.71 light years from a parallax of 880 ± 68 mas.
The most accurate early estimate came from Scottish astronomer David Gill and his American colleague William Lewis Elkin, who found a distance of 4.35 light years and a parallax of 750 ± 10 mas in 1885. A decade later, Scottish-born South African amateur astronomer Alexander W. Roberts calculated a distance of 4.29 light years from a parallax of 710 ± 50 mas.
In more recent times, Woolley et al. derived a distance of 4.39 light years from a parallax of 743 ± 7 mas in 1970, and van Altena et al. found a distance of 4.349 light years with a parallax of 749.9 ± 5.4 mas. Perryman et al. gave values of 4.395 light years and 742.12 ± 1.40 mas in 1997 and, in 1999, Swedish astronomer Staffan Söderhjelm calculated a distance of 4.366 light years with a parallax of 747.1 ± 1.2 mas.
In 2007, Floor van Leeuwen found a distance of 4.321 light years with a parallax of 754.81 ± 4.11 mas for Alpha Centauri A and 4.09 light years with a parallax of 796.92 ± 25.90 mas for Alpha Centauri B.
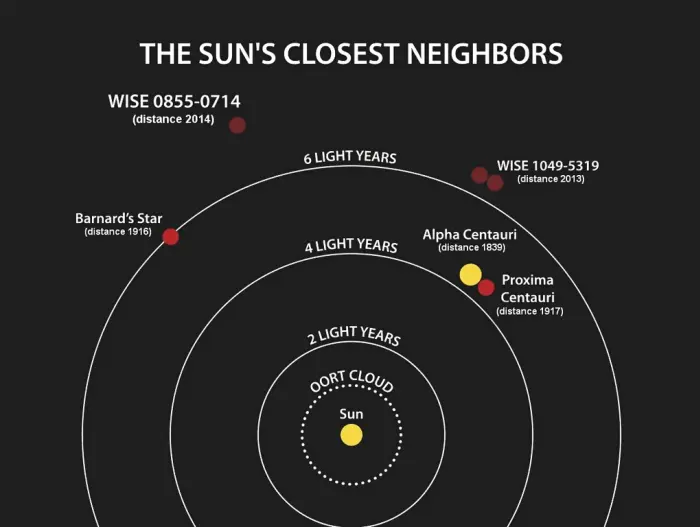
This diagram illustrates the locations of the star systems closest to the sun. The year when the distance to each system was determined is listed after the system’s name. Image: NASA/Penn State University (PD)
Planets
A total of six planets have been reported in the Alpha Centauri system. Only two of these planets have been confirmed. Both are orbiting Proxima Centauri. They are designated Proxima Centauri b (Alpha Centauri Cb) and Proxima Centauri d (Alpha Centauri Cd). These are the nearest known exoplanets to the Sun. Another candidate planet, Proxima Centauri c, has been detected in the Proxima system but its existence remains disputed.
Proxima b is believed to be a terrestrial planet, Proxima d is a sub-Earth, and Proxima c may be a super-Earth or mini-Neptune.
The discovery of Proxima b was announced in August 2016. The planet was detected by a team of scientists at the European Southern Observatory (ESO) using the radial velocity method. The planet has a mass of at least 1.055 Earth masses and a radius of 0.94 – 1.4 Earth radii. It orbits the host star from a distance of 0.04848 astronomical units and takes 11.18465 days to complete an orbit. With an equilibrium temperature of -39° C (234 K), it is a bit colder than Earth (-18° C/255 K).

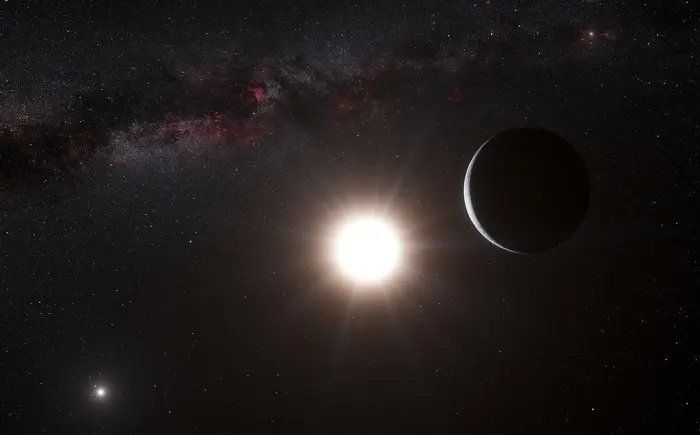
Artist’s impression of the exoplanet Proxima Centauri b shown as of an arid (but not completely water-free) rocky Super-Earth. This appearance is one of several possible outcomes of current theories regarding the development of this exoplanet, while the actual look and structure of the planet is known in no ways at this time. Proxima Centauri b is the closest exoplanet to the Sun and also the closest potentially habitable exoplanet as well. It orbits Proxima Centauri, a red dwarf with a surface temperature of 3040 K (thus hotter than light bulbs and therefore whiter, as depicted here). The Alpha Centauri binary system is shown in the background. Image: ESO/M. Kornmesser (CC BY 4.0)
The orbital distance of of 0.04848 AU places Proxima b in the habitable zone of Proxima Centauri, where liquid water may exist on the planet’s surface. However, the planet’s proximity to the host star makes it subject to flares and stellar winds more than 2,000 times stronger than those experienced by Earth. These would likely erode any atmosphere on the planet.
The discovery of Proxima Centauri c was reported in 2019. The controversial planet has a mass of about 7 Earth masses and orbits Proxima from a distance of about 1.49 astronomical units. It takes 1,928 days (5.28 years) to complete an orbit around the star. The planet may have a large ring system around it, detected in June 2020.
A third planet, Proxima Centauri d, was announced in February 2022. The planet orbits between the host star and the habitable zone. With only 26% of the Earth’s mass, it is one of the lightest planets discovered to date. It takes about 5.12338 days to complete an orbit around Proxima.
In addition to the planets orbiting Proxima, two planets have been reported around Toliman, Alpha Centauri B. In 2012, the discovery of Alpha Centauri Bb was announced, but the planet’s existence was disputed in 2015, when a different analysis showed that it most likely did not exist.
In 2013, another candidate exoplanet was detected around Alpha Centauri B. A possible transit event was observed that may correspond to a planet with a radius of about 0.92 Earth radii orbiting the star with a period of 20.4 days or less. If it exists, Alpha Centauri Bc is too close to its host star to harbour life.

This artist’s impression shows the planet orbiting the star Alpha Centauri B, a member of the triple star system that is the closest to Earth. Alpha Centauri B is the most brilliant object in the sky and the other dazzling object is Alpha Centauri A. Our own Sun is visible to the upper right. The tiny signal of the planet was found with the HARPS spectrograph on the 3.6-metre telescope at ESO’s La Silla Observatory in Chile. In October 2015, astronomers from the University of Oxford published a scientific paper disproving the existence of the planet. They observed that an identical statistical analysis of randomly-generated synthetic data gave the same results as the actual astronomical data. This led Xavier Dumusque, the lead author of the original paper, to concede “We are not 100 percent sure, but probably the planet is not there.” Credit: ESO/L. Calçada/N. Risinger (CC BY 4.0)
In 2025, astronomers reported the detection of Candidate 1 (C1), a potential planet orbiting Rigil Kentaurus (Alpha Centauri A). If confirmed, the planet will be given the designation Alpha Centauri Ab. It will be the nearest planet to Earth orbiting in the habitable zone of a Sun-like star.
A team led by Charles Beichman of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the NASA Exoplanet Science Institute at Caltech’s IPAC astronomy center, announced that observations with the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) aboard the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) provided the strongest evidence to date of a gas giant orbiting the Sun-like star. The study was published in two papers authored by Charles Beichman and Aniket Sanghi in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
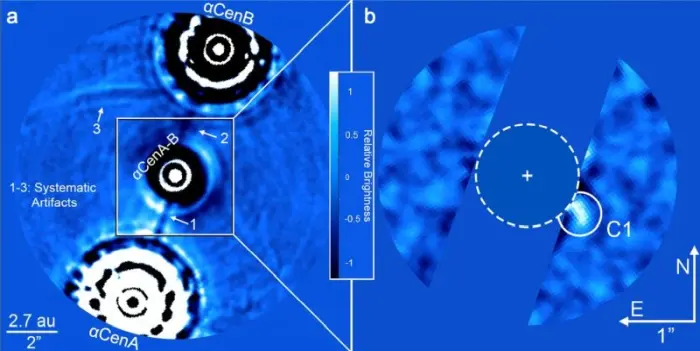
An image taken by the NEAR campaign as a proof-of-concept to allow for the direct detection of large planets around nearby stars. On the left are stars A and B blocked out with coronagraphs; On the right is a detail of the candidate’s detection. Credit: K. Wagner (CC BY 4.0)
Candidate 1 was directly imaged by the JWST. If it exists, the planet has 90 to 150 times the Sun’s mass – between the mass of Neptune and one-half the mass of Saturn – and a radius of 1.0 – 1.1 Jupiter radii. It orbits Alpha Centauri A at a distance of around 2 astronomical units with a period of 2 – 3 years and an eccentricity of 0.4. It has a temperature of 225 K (-48° C, -55° F).
Follow-up observations failed to detect the planet, but this may be because C1 had moved too close to its host star to be directly imaged. Observations with the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, which is expected to launch in May 2027, may provide additional evidence of the planet.
There may be additional planets orbiting Rigil Kentaurus and Toliman, either the individual stars or the Alpha Centauri AB binary, but none have been confirmed yet. Even though the system is a frequent target for observations and planet hunting, none of the studies have found evidence for the existence of other gas giants or brown dwarfs in the system.

This image shows the Alpha Centauri star system from several different ground- and space-based observatories: the Digitized Sky Survey (DSS), the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, and the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. Alpha Centauri A is the third brightest star in the night sky, and the closest Sun-like star to Earth. The ground-based image from DSS shows the triple system as a single source of light, while Hubble resolves the two Sun-like stars in the system, Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B. The image from Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument), which uses a coronagraphic mask to block the bright glare from Alpha Centauri A, reveals a potential planet orbiting the star. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, DSS, A. Sanghi (Caltech), C. Beichman (JPL), D. Mawet (Caltech), J. DePasquale (STScI) (CC BY 4.0)

This 3-panel image captures the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope’s observational search for a planet around the nearest Sun-like star, Alpha Centauri A. The initial image shows the bright glare of Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B, then the middle panel shows the system with a coronagraphic mask placed over Alpha Centauri A to block its bright glare. However, the way the light bends around the edges of the coronagraph creates ripples of light in the surrounding space. The telescope’s optics (its mirrors and support structures) cause some light to interfere with itself, producing circular and spoke-like patterns. These complex light patterns, along with light from the nearby Alpha Centauri B, make it incredibly difficult to spot faint planets. In the panel at the right, astronomers have subtracted the known patterns (using reference images and algorithms) to clean up the image and reveal faint sources like the candidate planet. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, A. Sanghi (Caltech), C. Beichman (JPL), D. Mawet (Caltech), J. DePasquale (STScI) (CC BY 4.0)
The habitable zone around Alpha Centauri A is between 1 and 2 astronomical units from the star and, to be in Alpha Centauri B’s habitable zone, a planet would need to have an orbital radius between 0.7 and 1.2 astronomical units.
Current estimates give a probability of about 75% of finding a terrestrial planet in the star system. A study published in 2009 found that planetesimal growth was only marginally possible in the innermost part of Toliman’s habitable zone, around 0.5 astronomical units from the star. Beyond this point the gravitational pull of the companion star would make planetesimal accretion impossible. However, binarity itself is not an obstacle to planet formation. More than 12% of all discovered exoplanets have been found in binary or multiple star systems.
In 2008, a theoretical study simulated the formation of planetary systems around Toliman and all simulations led to the formation of multiple planets, with at least one with a mass of 1-2 Earth masses orbiting at a distance of 0.5 to 1.5 astronomical units. The study suggested that a planet with 1.8 Earth masses could be reliably detected in the star’s habitable zone through radial velocity analysis.
Radial velocity measurements with the High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher (HARPS) did not detect any planets in the habitable zone of Alpha Centauri B, even though the HARPS spectrograph has the sensitivity and precision to detect a planet with 4 Earth masses.
A study published in 2014 found slight excesses of emissions at 24 μm (in the mid/far-infrared band) for both Alpha Centauri A and B. This may indicate the presence of thin circumstellar discs or dense interplanetary dust. Debris discs orbiting main sequence stars can indicate the presence of larger bodies.
A 2018 study based on observations with NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory concluded that any planets orbiting Alpha Centauri A and B are probably not being flooded with X-ray radiation to the point where life on the planets would be affected. In fact, any planets orbiting Alpha Centauri A would have better prospects of life than the planets orbiting the Sun.
Those prospects would be slightly worse around Alpha Centauri B than around the Sun, but not bad enough to pose a threat to life on any planets orbiting the star. The Chandra observations have captured the X-ray activity in the system over more than a decade, including the period during the closest approach.
Facts
Rigil Kentaurus, Alpha Centauri A, is one of the 58 bright stars selected for use in navigation. It is one of three navigational stars in the Centaurus constellation, along with Hadar (Beta Centauri) and Menkent (Theta Centauri). The three stars are among the 18 southern navigational stars with a declination between 30° S and 90° S. The group also includes Kaus Australis in Sagittarius, Shaula in Scorpius, Fomalhaut in Piscis Austrinus, Alnair in Grus, Peacock in Pavo, Acrux and Gacrux in Crux, Canopus, Miaplacidus and Avior in Carina, Atria in Triangulum Australe, Ankaa in Phoenix, Suhail in Vela, and Achernar and Acamar in Eridanus. Due to their location in the far southern sky, most of these stars are invisible to observers in mid-northern latitudes.
Alpha Centauri was mentioned in the Greek astronomer Ptolemy’s Almagest, a 2nd century star catalogue that also included the list of 48 Greek constellations. Ptolemy lived in Alexandria, Egypt (31° N), where the star was visible in his day. However, due to the Earth’s axial precession, Alpha Centauri now appears further south, at the declination -60° 51’, and it cannot be seen from locations north of the latitude 29° N.
The southern luminaries Alpha Centauri, Canopus and Achernar were largely unknown to European observers until the English geographer, mathematician and explorer Robert Hues published his work Tractatus de globis et eorum usu (Treatise on Globes and Their Use) in 1594. Hues made observations of the Southern Cross and other bright southern stars from the South Atlantic, during a voyage with the English explorer Thomas Cavendish. He published his discoveries in Tractatus de globis. He described the positions of Canopus, Achernar and Alpha Centauri as “in the sterne of Argo” (Canopus), “in the end of Eridanus” (Achernar), and “in the right foote of the Centaure” (Alpha Centauri).
Alpha Centauri was one of the first binary star systems to be discovered. Father Jean Richaud, a French Jesuit priest, resolved the two components from Pondicherry, India, in December 1689 while observing a comet. He noted, “On several occasions while looking at the comet through the 12-ft telescope I noticed at the feet of Centaur a most eastern and a more brilliant star, which was a double star, similar to the one at the feet of Crusade; the difference being that in the Crusade while looking through the telescope one star seemed particularly away from the other, whereas at the feet of Centaur, the two stars seemed to be practically touching each other, even though one could distinguish them easily.”
The high proper motion of the main pair was first reported by the British astronomer Manuel John Johnson, who observed the system from the island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. Johnson reported his findings to the Scottish astronomer Thomas Henderson at the Royal Observatory at the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa.
Henderson made further observations of Alpha Centauri AB between April 1832 and May 1833 and determined the system’s parallax, concluding that the stars were relatively close. He used French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille’s observations made in 1751 and 1752 and compared the differences between the star system’s measured positions in the 1750s and 1830s.
Even though the difference was considerable, Henderson withheld the results of his observations thinking that the values were too high to be accurate. He did not publish his findings until 1839, after the German astronomer and physicist Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel announced a parallax of 0.314 arcseconds for 61 Cygni, another nearby star (11.4 ly), in 1838. Even though Henderson measured the parallax of Alpha Centauri AB before Bessel, his work was not widely known at the time. For this reason, it is 61 Cygni that is usually cited as the first star to have its parallax measured, as well as the first star to have its distance estimated.
Due to their proximity to the Sun, the three stars in the Alpha Centauri system have a high proper motion (apparent motion across the background sky). The centre of mass of Alpha Centauri AB moves about 3620 milliarcseconds per year towards the west and 694 milliarcseconds per year towards the north. It moves about 6.1 arcminutes each century and 1.02 degrees each millennium. The system has a mean radial velocity of about 22.3 km/s in the direction of the Sun.
Even though it is the closest star system to the Sun, Alpha Centauri does not have the highest proper motion measured of any star. The three stars with the largest proper motion are Barnard’s Star, the second nearest star (system) to Earth at 5.958 light years, Kapteyn’s Star, the nearest known galactic halo star at 12.76 light years, and Groombridge 1830 (Argelander’s Star), another halo star, located at a distance of 29.93 light years. 61 Cygni, Keid (Omicron2 Eridani) and Epsilon Indi are among other stars that have a higher proper motion than Alpha Centauri.
The high proper motion of Alpha Centauri will gradually take it to Hadar’s position, and around the year 6200 CE, the two stars will form a conjunction and shine as a visual double. Even though it lies at a much greater distance (390 light years), Hadar (Beta Centauri) is a first-magnitude star, the 11th brightest star in the sky, and the conjunction of the two exceptionally bright stars will be a very rare event. Alpha Centauri will then move north of the Southern Cross and the constellation Vela toward the celestial equator and across Hydra, where it will be found around the year 26,700 CE.
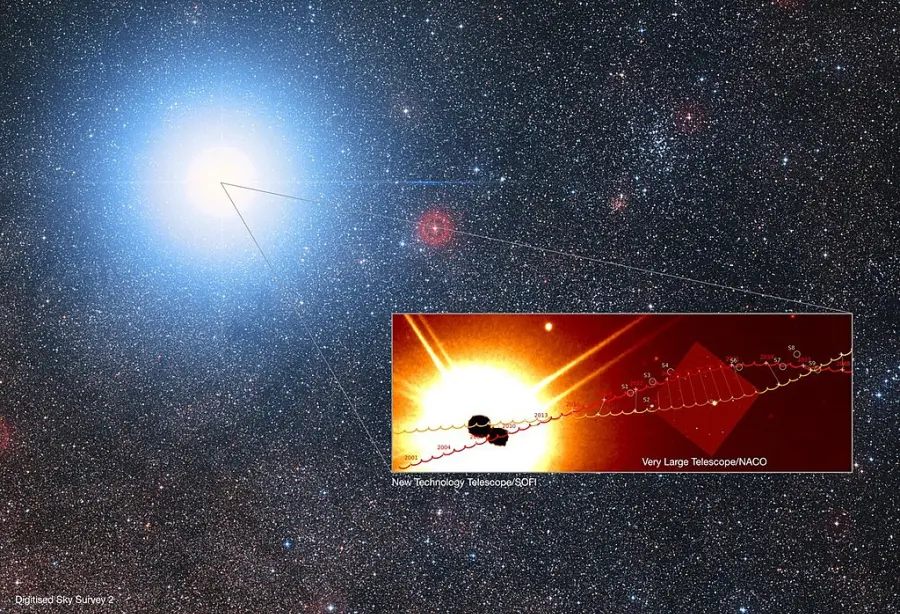
The predicted trajectory of Alpha Centauri A (orange) and B (red), superimposed onto an image taken with the SOFI instrument on ESO’s New Technology Telescope (NTT) and the NACO instrument on the VLT. It shows the conjunction with the star S5 (the brightest star in the NACO image). In the background a Digitised Sky Survey 2 image is shown. Credit: P. Kervella et al. (CNRS / U. de Chile / Observatoire de Paris / LESIA)/ESO (CC BY 4.0)
In the year 27,000 CE, the star will make its closest approach to the Sun, coming within 2.9 light years. At perihelion, it will shine at magnitude -0.86, which is a little brighter than Canopus is today (-0.74). It will not, however, outshine Sirius, which will keep getting brighter and stay the brightest star in the Earth’s sky for the next 210,000 years.
Proxima Centauri was discovered in 1915 by the Scottish astronomer Robert T. A. Innes from the Union Observatory in South Africa. Innes used a 9-inch refractor and a 10-inch astrographic camera and found a dim star that had the same high proper motion as Alpha Centauri AB. He believed that the star was closer to the Sun than Alpha Centauri, which was already considered the nearest star system, and gave it the name Proxima. However, he could not measure the star’s distance accurately with his equipment.
The distance of Proxima was definitively measured by the American astronomer Harold Lee Alden from the Yale observatory station in Johannesburg. Alden’s work confirmed that Proxima was indeed the nearest star to the Sun.
The orbital elements of Alpha Centauri AB were first calculated with some accuracy in 1926 by the South African astronomer William Stephen Finsen, who made his observations from the Union Observatory in South Africa, where Robert Innes had discovered Proxima Centauri over a decade earlier. Finsen gave an orbital period of 80.089 years for the system with a major axis of 35.33 arcseconds.
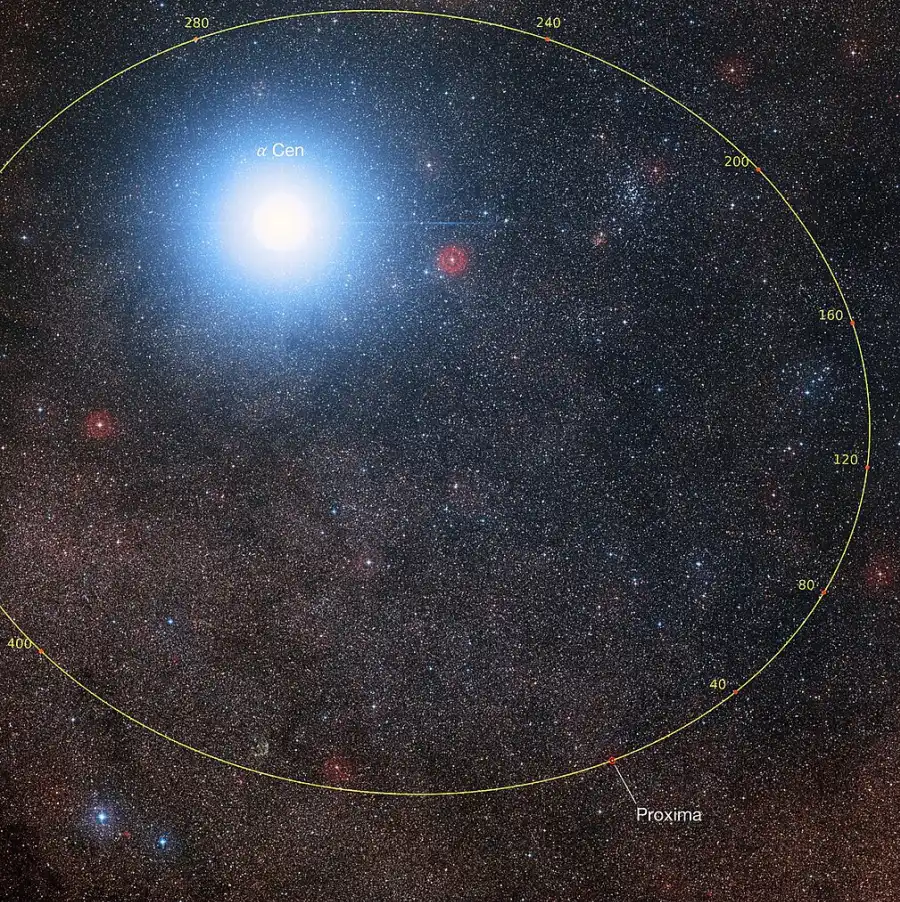

Orbital plot of Proxima Centauri showing its position with respect to Alpha Centauri over the coming millenia (graduations are in thousands of years). The large number of background stars is due to the fact that Proxima Cen is located very close to the plane of the Milky Way. Credit: P. Kervella (CNRS/U. of Chile/Observatoire de Paris/LESIA), ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2, D. De Martin/M. Zamani (CC BY 4.0)
The currently accepted orbital period of 79.91 years is credited to Belgian astronomer Dimitri Pourbaix and his team, who derived the value based on their observations at Université libre de Bruxelles in Belgium in 2002.
Alpha Centauri lies within the G-Cloud complex, a neighbouring interstellar cloud to the Local Interstellar Cloud. The Sun is believed to be either in the Local Interstellar Cloud or in the area between the two clouds, but it is moving towards the G-Cloud. The G-Cloud also contains Altair, the brightest star in the constellation Aquila and the 12th brightest star in the sky, located at a distance of 16.73 light years from the Sun.
The nearest star or star system to Alpha Centauri is not the Sun, but Luhman 16, a binary system composed of two brown dwarfs. Luhman 16 is located only 3.577 light years from Alpha Centauri AB, 3.520 light years from Proxima Centauri, and 6.5102 light years from the Sun. The system does not appear very close to Alpha Centauri in the sky. It lies in the constellation Vela, south of Mu Velorum and north of the Carina Nebula in Carina. Luhman 16 is the third nearest star system to the Sun, after Alpha Centauri and Barnard’s Star, and its two components are the nearest known brown dwarfs.
An observer on a hypothetical planet in the Alpha Centauri system would see pretty much the same sky that observers on Earth see. However, they would see Centaurus without its brightest star. Alpha Centauri AB would appear as a close visual double that could be resolved without binoculars most of the time. The two components would have apparent magnitudes of -6.5 (Rigil Kentaurus) and -5.2 (Toliman).
From a hypothetical planet in the Alpha Centauri system, the Sun would appear as a first-magnitude star in the constellation Cassiopeia. At magnitude +0.47, it would be as bright from Alpha Centauri as Achernar is from Earth. It would appear in the same line of sight as the Heart Nebula, east of Segin (Epsilon Cassiopeiae), the leftmost star of Cassiopeia’s W, and it would give Cassiopeia’s W a /W shape.
A view of the sky towards the Sun as seen from the vicinity of Alpha Centauri A. The Sun would be in the constellation Cassiopeia as viewed from there. Generated by the author using Celestia 1.4.1, which is GPL.
As the nearest star system to the Sun, Alpha Centauri is a target for several interstellar exploration missions. These missions are still in the concept stage and will likely remain so in the foreseeable future because the technology that would reduce travel time to the star system does not yet exist. The existing spacecraft would take several millennia to get there.
In 2017, NASA introduced a project aiming to launch an interstellar probe by the year 2069 – on the 100th anniversary of the Moon landing – to search for biosignatures on planets in the Alpha Centauri system. Even though the mission concept is in the preliminary stage, scientists and engineers have suggested the use of solar sails propelled by high energy lasers to reduce travel time.
Solar sails are the method of choice for the well-funded Breakthrough Starshot project, announced on April 12, 2016. The project was developed by the physicist and entrepreneur Yuri Milner, physicist Stephen Hawking, and internet entrepreneur Mark Zuckerberg, with the goal to develop a fleet of solar sail spacecraft that could be sent to the Alpha Centauri system. A flyby mission to Proxima Centauri b was proposed after the planet’s existence was confirmed in August 2016.
In January 2017, Breakthrough Initiatives started collaborating with the European Southern Observatory (ESO) to search for planets in the habitable zones of the Alpha Centauri system. The Breakthrough Starshot concept would entail launching a mothership with about a thousand small, centimetre-sized spacecraft to high-altitude Earth orbit, then using ground-based (or space-based) lasers to focus a light beam on the crafts’ sails to accelerate them. The journey would take 20-30 years and a return message to Earth would take only about four years. The first craft may launch by the year 2036.
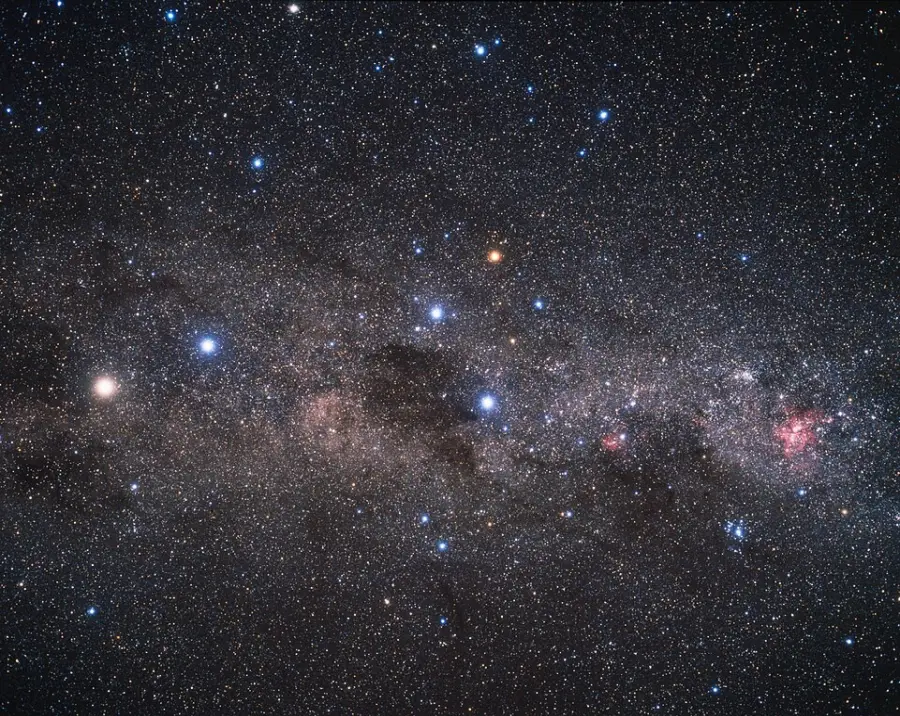

This wide-field image shows the Milky Way stretching across the southern sky. The beautiful Carina Nebula (NGC 3372) is seen at the right of the image glowing in red. It is within this spiral arm of our Milky Way that the bright star cluster NGC 3603 resides. At the centre of the image is the constellation of Crux (The Southern Cross). The bright yellow/white star at the left of the image is Alpha Centauri, in fact a system of three stars, at a distance of about 4.4 light-years from Earth. The star Alpha Centauri C, Proxima Centauri, is the closest star to the Solar System. Image credit: A. Fujii (CC BY 4.0)
Like many other bright and nearby stars, Alpha Centauri has been used in countless works of fiction, including literature, film and television, comic books, and video games.
Notable uses in literature include a poem by Jan Neruda in the collection “Cosmic Songs” (1878), the short story “Proxima Centauri” (1935) by Murray Leinster, Isaac Asimov’s short story “Homo Sol” (1940), Larry Niven’s “Like Banquo’s Ghost” (1968), Frederick Pohl’s “The Gold at the Starbow’s End” (1972), and “Far Centaurus” (1944) by A. E. van Vogt, the novels Revolt on Alpha C (1955) by Robert Silverberg, Stanislaw Lem’s The Magellanic Cloud (1955), Gordon R. Dickson’s Childe Cycle (1959) series, Edmund Cooper’s Seed of Light (1959), Leigh Brackett’s Alpha Centauri or Die! (1963), Philip K. Dick’s Clans of the Alphane Moon (1964), Larry Niven’s The Man-Kzin Wars (1966), M. John Harrison’s The Centauri Device (1975), James P. Hogan’s Voyage from Yesteryear (1982), William Gibson’s Neuromancer (1984), Isaac Asimov’s Foundation and Earth (1986), Arthur C. Clarke’s The Songs of Distant Earth (1986), Poul Anderson’s Harvest of Stars (1994), S. M. Stirling’s Drakon (1996), John Barnes and Buzz Aldrin’s Encounter with Tiber (1996), Mary Doria Russell’s The Sparrow (1996), Robert J. Sawyer’s Factoring Humanity (1998), Michael Ely’s Centauri Dawn (2000), Paul Levinson’s Borrowed Tides (2001), Liu Cixin’s Three Body (2008), Alastair Mayer’s Alpha Centauri trilogy (2016-17), and Kevin Emerson’s The Oceans Between Stars (2018).
Memorable uses and mentions in television include the series Lost in Space (1965-68), the episodes “Tomorrow is Yesterday” and “Metamorphosis” (1967) of Star Trek: The Original Series, the episode “Past Tense, Part 1” of Star Trek: Deep Space Nine, the serials “The Curse of Peladon” (1972) and “The Monster of Peladon” (1974) of Doctor Who, the episode “The Golden Man” (1981) of Buck Rogers in the 25th Century, and the episode “No Surrender, No Retreat” of Babylon 5.
In film, the star system was used in Event Horizon (1997), Lost in Space (1998), Impostor (2002), Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy (2005), Avatar (2009), and Princess of Mars (2012).
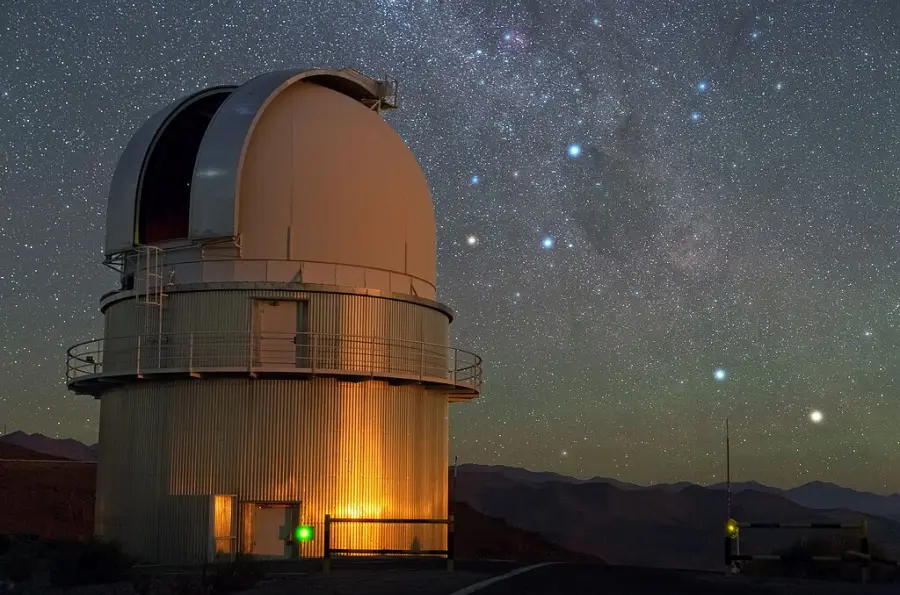

In the sky above ESO’s La Silla Observatory, the Southern Cross is clearly visible just to the right of the dome of the Danish 1.54-metre telescope, and to the lower right of the image, two stars sparkle in the amazingly dark sky. From right to left, these are Alpha and Beta Centauri. Alpha Centauri is a multiple star, the nearest star system to Earth. Credit: Y. Beletsky (LCO)/ESO (CC BY 4.0)
Name
All three components of the Alpha Centauri system have formal names. The primary component, Alpha Centauri A, is called Rigil Kentaurus, Alpha Centauri B is also known as Toliman, and Alpha Centauri C has the formal name Proxima Centauri.
The name Rigil Kentaurus (pronunciation: /ˈraɪdʒəl kɛnˈtɔːrəs/) comes from the Arabic phrase Rijl al-Qinṭūrus, meaning “the foot of the Centaur.” It is the star’s traditional name and it refers to its position in the constellation. The name was approved by the International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) on November 6, 2016. It has also been abbreviated to Rigil Kent or just Rigil. It has the same etymology as Rigel, the name of Beta Orionis, the bright star that marks the foot of Orion.
The name Toliman (pronunciation: /ˈtɒlɪmæn/) comes from the Arabic aẓ-Ẓalīmān or aṭ-Ṭhalīmān, meaning “the (two male) ostriches.” It refers to an asterism, “the ostriches,” in which Alpha Centauri was the brightest star. The name was once colloquially used for the entire star system. The IAU approved it for Alpha Centauri B on August 10, 2018.
The name Proxima Centauri (pronunciation: /ˈprɒksɪmə sɛnˈtɔːraɪ/) comes from a suggestion made by the Scottish astronomer Robert T. A. Innes. Innes discovered the star in 1915 and proposed the name Proxima Centaurus, believing that the star was closer to us than Alpha Centauri AB. The name means “the nearest (star) of Centaurus.” The version with the genitive Centauri became widely used later and was approved by the IAU on August 21, 2016.
Alpha Centauri was known by many other names across different cultures throughout history. It was called Bungula (pronunciation: /ˈbʌŋɡjuːlə/), possibly derived from the letter β (beta) and the Latin ungula, meaning “hoof.”
Alpha and Beta Centauri (Hadar) are known as the Southern Pointers, or simply the Pointers in the southern hemisphere. The two stars point in the direction of the Southern Cross, a conspicuous southern asterism commonly used to find true south.
In traditional Chinese astronomy, Alpha Centauri was known as 南門二 (Nán Mén Èr), the Second Star of the Southern Gate. The Chinese Southern Gate asterism was formed by Alpha Centauri with Epsilon Centauri. It was part of the Horn mansion, which represented the horns of the Azure Dragon.
Alpha Centauri has played a prominent role in many cultures in the southern hemisphere. The Bushmen in South Africa called Alpha and Beta Centauri Two Men That Once Were Lions. In Australia, the Boorong people of northwest Victoria called the stars Bermbermgle, after two brothers known for their courage. In local lore, the brothers helped do away with Tchingal, the Emu, represented by the nearby dark Coalsack Nebula. The Wotjobaluk people of Victoria had a similar legend and called the brothers Bram-bram-bult.
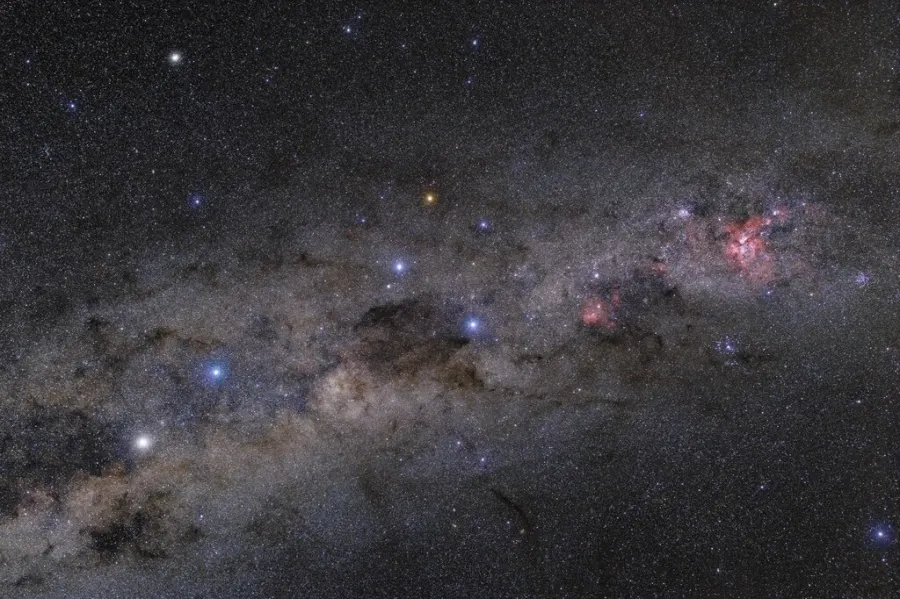

Part of the southern Milky Way, around the constellations of Centaurus, Crux and Carina. In the center of the image, the majestic Southern Cross (Crux) constellation, symbol of ESO, takes the central stage with dark Coalsack Nebula close by. On the left, brightest stars of Centaurus can be seen with theit typical colours. The brighter one is Alpha Centauri, one of the closest stars to our Sun. Right part of the view belngs to prominent Carina Nebula, one of the most significant of its type in the whole sky. Credit: ESO/P. Horálek (CC BY 4.0)
Location
Alpha Centauri is very easy to find. It lies near Hadar, the 11th brightest star in the sky, and the Southern Cross, a prominent southern asterism formed by the bright stars Acrux, Mimosa, Gacrux, Imai and Ginan in the constellation Crux.
However, due to its location in the far southern sky, Alpha Centauri stays invisible to observers in mid-northern latitudes. Observers south of the latitude 29° S can see Alpha Centauri throughout the year because the star is circumpolar, i.e. it never sinks below the horizon. Observers north of the latitude 29° N, however, never see the star because it never rises above the horizon. Alpha Centauri can be seen from locations between the latitude 29° N and the equator, but only at certain times of the year and it always stays close to the southern horizon.
Location of Alpha Centauri, image: Stellarium
Alpha Centauri culminates, i.e. it reaches the highest point in the sky, at midnight on April 24 and around 9 pm on June 8.
Unlike the bright Alpha Centauri AB, Proxima Centauri is not very easy to find. The faint red dwarf lies 2.2 degrees – about four full Moons away – from the main pair. With an apparent magnitude of 11.1, it requires medium-sized telescopes to be seen.
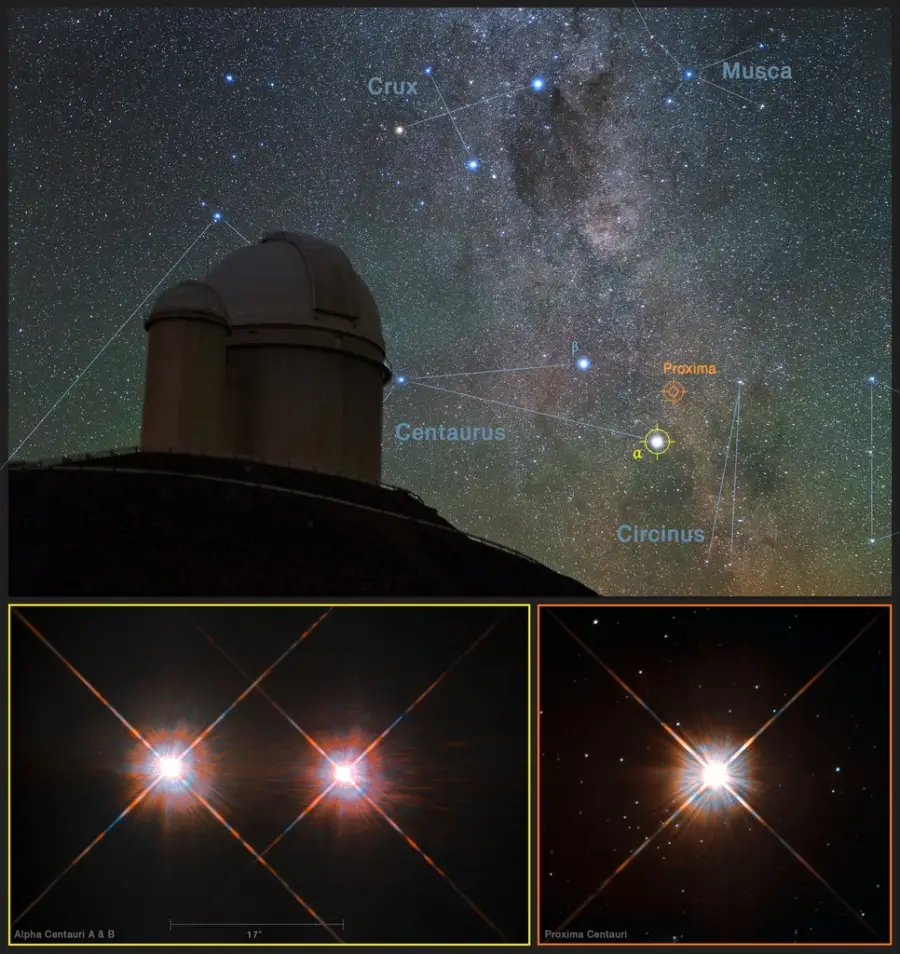

This picture combines a view of the southern skies over the ESO 3.6-metre telescope at the La Silla Observatory in Chile with images of the stars Proxima Centauri (lower-right) and the double star Alpha Centauri AB (lower-left) from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Proxima Centauri is the closest star to the Solar System and is orbited by the planet Proxima b, which was discovered using the HARPS instrument on the ESO 3.6-metre telescope. Image credit: ESO (CC BY 4.0)
Alpha and Beta Centauri are known as the Southern Pointers. They point the way to the Southern Cross, an asterism commonly used to find the south celestial pole. A line drawn from Alpha through Beta Centauri leads to Gacrux, the top star of the Southern Cross, which lies about 4.5 degrees to the west.
Formed by two first-magnitude and one second-magnitude star, the Southern Cross is easy to find even without the Pointers, but the Centaurus stars help distinguish it from the False Cross, a similar asterism formed by Alsephina (Delta Velorum), Markeb (Kappa Velorum), Avior (Epsilon Carinae), and Aspidiske (Iota Carinae). The south celestial pole lies about halfway between Hadar and Achernar, the ninth brightest star in the sky.

Alpha and Beta Centauri, the Southern Cross, Achernar and south celestial pole, image: Stellarium
Another way to locate the pole is to extend a line from Gacrux through Acrux and draw another line at a right angle to the line connecting the Pointers. The pole is near the point where the two lines cross.
Alpha Centauri can be used to find several deep sky objects that appear in the vicinity. The open clusters NGC 5617 (the Dracula Cluster) and Trumpler 22 appear around a degree west-northwest of the star, in the direction of Hadar. The open cluster NGC 5606 lies north of NGC 5617, on the imaginary line connecting Alpha and Epsilon Centauri.
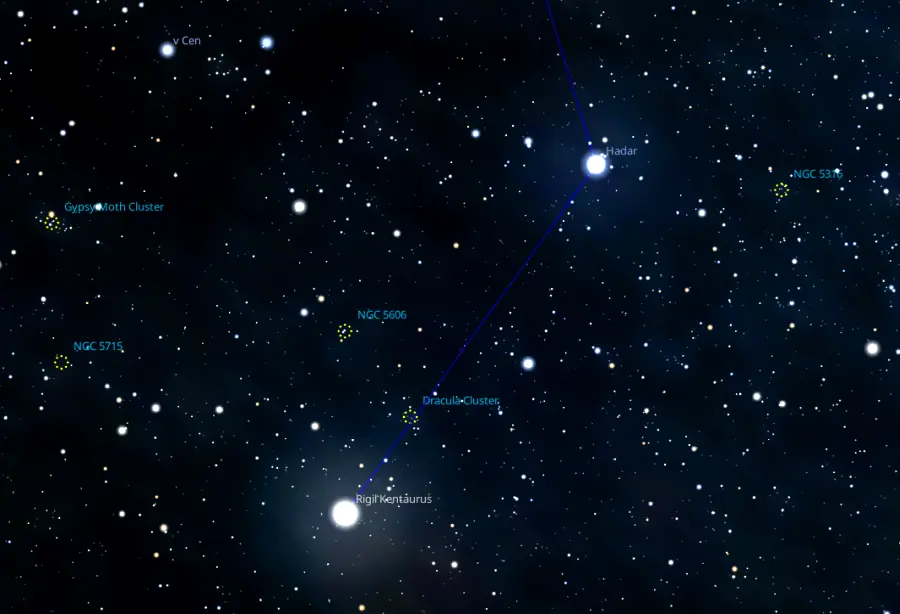
Alpha Centauri, Beta Centauri, NGC 5606 and NGC 5617, image: Stellarium
Constellation
Alpha Centauri is located in the constellation Centaurus. The celestial Centaur has been known since ancient times. It is one of the 48 Greek constellations, first listed by Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. It is the ninth largest of all 88 constellations, occupying 1,060 square degrees of the southern sky.
Centaurus is also one of the brightest constellations. It contains 10 stars brighter than magnitude 3.00, including Alpha Centauri and Hadar (Beta Centauri), the third and 11th brightest stars in the sky. The constellation is also home to the supergiant or hypergiant star HR 5171 (V766 Centauri), one of the largest stars known, the chemically peculiar Przybylski’s Star, and the Diamond Star (Lucy), a white dwarf with a crystallized carbon core.
Other notable stars in Centaurus include the orange giant Menkent (Theta Centauri), the A-type binary system Gamma Centauri, the blue giants Epsilon Centauri and Lambda Centauri, the Gamma Cassiopeiae and Lambda Eridani variable Eta Centauri, the hot blue binary systems Zeta Centauri (Leepwal) and Nu Centauri (Heng), the hot blue shell star Delta Centauri, the Mira variable R Centauri, and the A-type star Kulou (Iota Centauri).
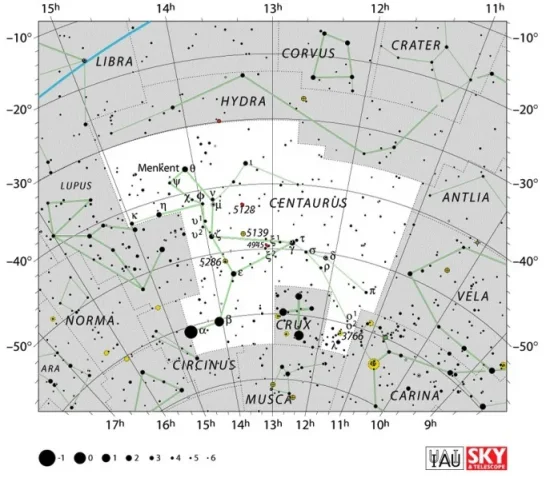
Centaurus constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Centaurus contains many interesting deep sky objects. These include Omega Centauri, the largest (36′.3), brightest (mag. 3.9) and most massive globular cluster known in the Milky Way, the starburst galaxy Centaurus A, one of the brightest galaxies in the sky (mag. 6.84), the spiral galaxies NGC 4945 and NGC 4622 (the Backward Galaxy), the irregular galaxy NGC 5253, a member of the Centaurus A/M83 Group, the elliptical galaxy NGC 4696, the brightest galaxy in the Centaurus Cluster, the polar-ring lenticular galaxy NGC 4650A, the open clusters NGC 3766 and NGC 5460, the Lambda Centauri Nebula (IC 2944, Running Chicken Nebula), the protoplanetary nebula ESO 172-7 (the Boomerang Nebula), and the bright planetary nebula NGC 3918, also known as the Blue Planetary or the Southerner.
While it stays mostly invisible to northern observers, Centaurus is circumpolar in the southern hemisphere, i.e. it never falls below the horizon and can be seen throughout the year.
The best time of the year to see the stars and deep sky objects in the constellation is during the month of May, when it rises high above the horizon in the early evening. The entire constellation is visible from locations between the latitudes 25° N and 90° S.
The 10 brightest stars in Centaurus are Alpha Centauri (mag. -0.27), Hadar (Beta Cen, mag. 0.61), Menkent (Theta Cen, mag. 2.06), Gamma Centauri (mag. 2.17), Epsilon Centauri (mag. 2.30), Eta Centauri (mag. 2.35), Leepwal (Zeta Cen, mag. 2.55), Delta Centauri (mag. 2.57), Kulou (Iota Cen, mag. 2.73), and Lambda Centauri (mag. 3.13).
Alpha Centauri
| Apparent magnitude | -0.27 |
| Parallax | 750.81 ± 0.38 mas |
| Radial velocity | -22.3 ± 0.9 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: -3608 ± 30 mas/yr |
| Dec.: 686 ± 25 mas/yr | |
| Constellation | Centaurus |
| Right ascension | 14h 39m 36.50s |
| Declination | -60° 50′ 02.3″ |
| Names and designations | Alpha Centauri, Alpha Cen, α Centauri, α Cen, SAO 252838, FK5 538, GJ 559, GC 19728, GCRV 8519, CD-60 5293, CD−60°5483, CPD-60 5483, Ci 20 875, LPM 534, CSI-60 5483 43, CCDM J14396-6050, RHD 1, LDS 494AB, PM 14362-6038, 1E 143556-6037.3, 1E 143555-6037.6, 2E 3308, 2E 1435.9-6037, 1ES 1435-60.6, 2EUVE J1439-60.8, EUVE J1439-60.8, IRAS 14359-6037, RE J1439-605, RE J143944-605008, 2RE J1439-605, 2RE J143941-605000, RX J1439.5-6050, 1RXS J143940.4-605020, GES J14392972-6049560, uvby98 100128620, 2XMM J143933.0-605008, IDS 14328-6025 AB, WDS J14396-6050AB, WDS J14403-6051AB |
Rigil Kentaurus – Alpha Centauri A
| Spectral class | G2V |
| U-B colour index | +0.24 |
| B-V colour index | +0.71 |
| Apparent magnitude | 0.01 |
| Absolute magnitude | 4.38 |
| Distance | 4.344 ± 0.002 light-years (1.3319 ± 0.0007 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 750.81 ± 0.38 mas |
| Radial velocity | −15.252000 ± 0.167000 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: −3679.25 ± 3.89 mas/yr |
| Dec.: 473.67 ± 3.24 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 1.0788 ± 0.0029 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.5059 ± 0.0019 L☉ |
| Radius | 1.2175 ± 0.0055 R☉ |
| Temperature | 5,804 ± 13 K |
| Metallicity | 0.20 ± 0.01 dex |
| Age | 5.26 ± 0.95 billion years |
| Rotational velocity | 2.7 ± 0.7 km/s |
| Rotation | 28.3 ± 0.5 days |
| Surface gravity | 4.30 cgs |
| Right ascension | 14h 39m 36.49400s |
| Declination | −60° 50′ 02.3737″ |
| Names and designations | Rigil Kentaurus, Rigil Kent, Alpha Centauri A, α Cen A, Alpha1 Centauri, α1 Centauri, HD 128620, HR 5459, HIP 71683, SAO 252838, LHS 50, GJ 559 A, PLX 3309.00, GCTP 3309.00, GCRV 8517, LFT 1127, LTT 5806, NLTT 37984, PPM 360911, CD-60 5293A, CPD-60 5483A, CSI-60 5483 41, SKY# 26645, SPOCS 610, CNS5 3627, PM 14362-6038A, TD1 17606, PMSC 14328-6025A, GEN# +1.00128620A, RHD 1A, GALAH 140708001701306, SBC7 520, SBC9 815, Zkh 209, TIC 471011145, WEB 12354, 2MASS J14393592-6050069, TYC 9007-5849-1, CCDM J14396-6050A, IDS 14328-6025 A, WDS J14396-6050A |
Toliman – Alpha Centauri B
| Spectral class | K1V |
| U-B colour index | +0.68 |
| B-V colour index | +0.88 |
| Apparent magnitude | 1.33 |
| Absolute magnitude | 5.71 |
| Distance | 4.344 ± 0.002 light-years (1.3319 ± 0.0007 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 750.81 ± 0.38 mas |
| Radial velocity | -22.586 ± 0.0001 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: −3614.39 ± 20.48 mas/yr |
| Dec.: 802.98 ± 19.52 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 0.9092 ± 0.0025 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.4981 ± 0.0007 L☉ |
| Radius | 0.8591 ± 0.0036 R☉ |
| Temperature | 5,207 ± 12 K |
| Metallicity | 0.24 ± 0.01 dex |
| Age | 5.26 ± 0.95 billion years |
| Rotational velocity | 1.1 ± 0.8 km/s |
| Rotation | 36.7 ± 0.3 days |
| Surface gravity | 4.37 cgs |
| Right ascension | 14h 39m 35.06311s |
| Declination | −60° 50′ 15.0992″ |
| Names and designations | Toliman, Alpha Centauri B, α Cen B, Alpha2 Centauri, α2 Centauri, HD 128621, HR 5460, HIP 71681, GJ 559 B, LHS 51, GCRV 8518, LFT 1128, LTT 5807, NLTT 37985, SKY# 26644, CD-60 5293B, CPD-60 5483B, CSI-60 5483 42, PM 14362-6038B, PMSC 14328-6025B, SPOCS 609, Zkh 210, GEN# +1.00128621, RAVE J143935.1-605014, TIC 471011144, TYC 9007-5848-1, CCDM J14396-6050B, IDS 14328-6025 B, WDS J14396-6050B |
Proxima Centauri – Alpha Centauri C
| Spectral class | M5.5Ve |
| Variable type | UV Ceti and BY Draconis |
| U-B colour index | 1.26 |
| B-V colour index | 1.82 |
| V-R colour index | 1.68 |
| R-I colour index | 2.04 |
| J-H colour index | 0.522 |
| J-K colour index | 0.973 |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 10.43 – 11.11 |
| Apparent magnitude (U) | 14.21 |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 12.95 |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.13 |
| Apparent magnitude (R) | 9.45 |
| Apparent magnitude (I) | 7.41 |
| Apparent magnitude (J) | 5.357 ± 0.023 |
| Apparent magnitude (H) | 4.835 ± 0.057 |
| Apparent magnitude (K) | 4.384 ± 0.033 |
| Absolute magnitude | 15.60 |
| Distance | 4.2465 ± 0.0003 light-years (1.30197 ± 0 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 768.0665 ± 0.0499 mas |
| Radial velocity | −20.578199 ± 0.004684 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: −3781.741 ± 0.031 mas/yr |
| Dec.: 769.465 ± 0.051 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 0.1221 ± 0.0022 M☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 0.001567 ± 0.000020 L☉ |
| Luminosity (visual, LV) | 0.00005 L☉ |
| Radius | 0.1542 ± 0.0045 R☉ |
| Temperature | 2,992 K (2,945 – 3,041 K) |
| Metallicity | 0.21 dex |
| Age | 4.85 billion years |
| Rotational velocity | < 0.1 km/s |
| Rotation | 83.2 ± 1.6 days |
| Surface gravity | 5.20 ± 0.23 cgs |
| Right ascension | 14h 29m 42.9461331854s |
| Declination | −62° 40′ 46.164680672″ |
| Names and designations | Proxima Centauri, Proxima Cen, Alpha Centauri C, α Cen C, V645 Centauri, V645 Cen, HIP 70890, GJ 551, LTT 5721, NLTT 37460, PLX 3278.00, LPM 526, LHS 49, LFT 1110, Ci 20 861, AP J14294291-6240465, CSV 2142, PM 14263-6228, PM J14297-6240, PMSC 14328-6025C, WISEA J142937.35-624038.3, CNS5 3591, CSI-62-14263, JP11 5156, JP11 5155, JP11 5187, 1E 1425.9-6228, 2E 1426.0-6227, 2E 3278, 1ES 1426-62.4, EUVE J1430-62.6, EUVE J1429-62.6, 2EUVE J1429-62.6, RE J1429-624, RE J142950-624056, 2RE J142946-624031, RX J1429.7-6240, 1RXS J142947.9-624058, Zkh 211, GEN# +6.10010551, GEN# +6.00105721, IRAS 14260-6227, 2MASS J14294291-6240465, TIC 388857263, TIC 1019422535, [FS2003] 0708, [GKL99] 301, [RHG95] 2291, [AOP94] 6, Gaia DR2 5853498713160606720, Gaia DR3 5853498713190525696, CCDM J14396-6050C, WDS J14396-6050C |