Alrakis, Mu Draconis (μ Dra), is the primary component in a multiple star system located approximately 89 light-years away in the constellation Draco. With an apparent magnitude of 4.92, it is only the 33rd brightest star in Draco. It appears near the asterism that represents the head of the Dragon.
Star system
The Mu Draconis system is composed of Mu Draconis A, the binary pair Mu Draconis Ba and Bb (Mu Draconis B), and Mu Draconis C. The brighter components, Mu Draconis A and B, shine at magnitudes 5.66 and 5.69, and have a combined apparent magnitude of 4.92.
The primary component, Mu Draconis A, is a white main sequence star of the spectral type F7V. It has a mass of 1.35 solar masses.
Mu Draconis Ba is also an F-type main sequence star. It has a mass of 1.30 solar masses. Its close companion, Mu Draconis Bb, is much less massive, with a mass of 0.2 solar masses.
Mu Draconis C has a similar proper motion to Mu Draconis A and B but is separated by 13.2 arcseconds from the bright pair. It is a 14th-magnitude star with a mass 29% that of the Sun.
The two components of Mu Draconis B have an orbital period of 2,270 days. They are separated by 2 arcseconds and can be resolved in telescopes with an aperture of at least 6 centimetres (2.36 inches).

Alrakis (Mu Draconis), image: Wikisky
Facts
In Arabic astronomy, Alrakis was part of an asterism known as the Mother Camels (Al ʽAwāïd). The asterism was formed by Alrakis and the four brighter stars that mark the head of Draco: Eltanin (Gamma Draconis), Rastaban (Beta Draconis), Grumium (Xi Draconis), and Kuma (Nu Draconis). The Latin name for the Mother Camels was Quinque Dromedarii.
The nearby Athebyne and Aldhibah (Eta and Zeta Draconis) represented two wolves or hyenas stalking the camel’s foal, represented by the fainter Alruba (HD 161693), which appears at the centre of the Mother Camels asterism. Alrakis represented a camel running to join its four companions. The name Alruba is derived from the Arabic word for “the foal,” and the names Athebyne and Aldhibah refer to the two wolves or hyenas.
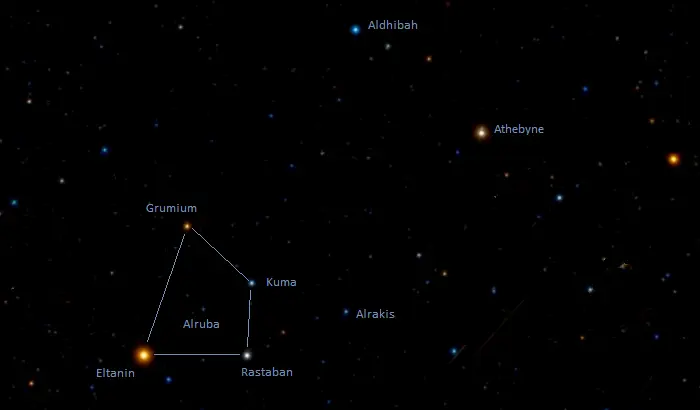
The Two Wolves and the Mother Camels, image: Wikisky
Name
The name Alrakis (pronunciation: /ælˈreɪkɪs/) comes from the Arabic word al-rāqiṣ, meaning “the trotting (camel)” or “the dancing one.” It was historically also spelled Errakis.
The name was approved by the International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) on February 1, 2017. It formally applies only to the component Mu Draconis A but has traditionally been used for the whole star system.
The name Alrakis inspired the name of the fictional planet Arrakis in Frank Herbert’s science fiction series Dune. In the novels, Arrakis is the third planet orbiting Canopus. It is the home of the Fremen people and the Imperial Capital of the Atreides Empire. Herbert chose the name because it was derived from the Arabic word for “the dancer.”
Location
Alrakis is easy to find in good conditions, but shining at magnitude 4.92, it is difficult to see in light-polluted skies. The star lies near the asterism that represents the head of the Dragon and appears as its extension.
The Head of Draco can be found using the brighter stars of the Northern Cross in Cygnus. A line extended through the beam of the Cross leads to Eltanin and Rastaban, the stars that mark the eyes of the Dragon.
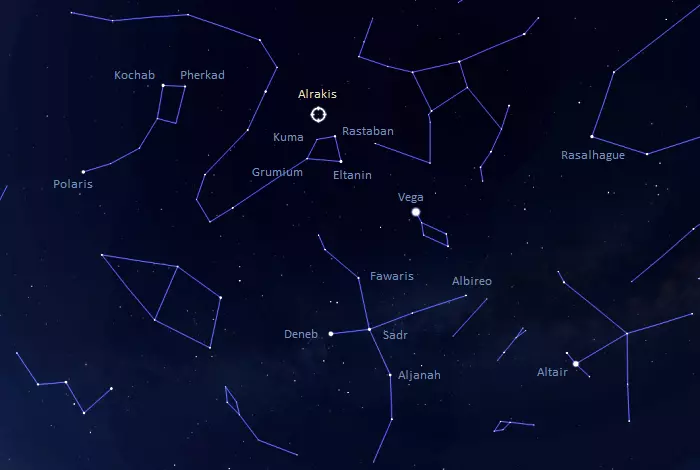
The location of Alrakis, image: Stellarium
Constellation
Alrakis is located in the constellation Draco. The celestial Dragon is one of the 48 Greek constellations first catalogued by Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. In Greek mythology, it is associated with the dragon Ladon, who guarded the gardens of the Hesperides and met its end at the hands of Heracles.
The constellation Draco is circumpolar to observers in the northern hemisphere, i.e. it never falls below the horizon and is visible throughout the year near the north celestial pole. In the southern hemisphere, Draco stays very close to the northern horizon and is largely invisible from locations that are not close to the equator.
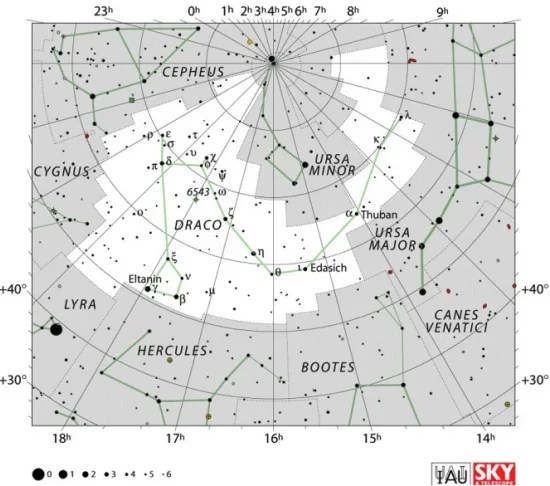
Draco constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine
Draco is the eighth largest of the 88 constellations. It covers an area of 1,083 square degrees. Despite its size, it is not particularly conspicuous. The orange giant Eltanin (Gamma Draconis), the constellation’s brightest star, has an apparent magnitude of 2.24.
Other notable stars in Draco include the yellow supergiant or bright giant Rastaban (Beta Draconis), the yellow giants Athebyne (Eta Draconis) and Omicron Draconis, the blue giant Kappa Draconis, the orange giant Edasich (Iota Draconis), and the white subgiant Thuban (Alpha Draconis). Alpha, Kappa and Iota Draconis are in the exclusive group of stars that take their turn as the North Star during the Earth’s axial precession cycle.
Draco hosts several interesting deep sky objects. These include the planetary nebula NGC 6543, also known as the Cat’s Eye Nebula, the Spindle Galaxy (Messier 102, NGC 5866), the massive galaxy cluster Abell 2218, the Tadpole Galaxy (Arp 188), and the Draco Dwarf.
The best time of the year to observe the stars and deep sky objects in Draco is during the month of July, when the constellation is high in the evening sky. The entire constellation can be seen from locations north of the latitude 15° S.
The 10 brightest stars in Draco are Eltanin (Gamma Dra, mag. 2.23), Athebyne (Eta Dra, mag. 2.73), Rastaban (Beta Dra, mag. 2.79), Altais (Delta Dra, mag. 3.07), Aldhibah (Zeta Dra, mag. 3.17), Edasich (Iota Dra, mag. 3.29), Chi Draconis (mag. 3.57), Thuban (Alpha Dra, mag. 3.6452), Grumium (Xi Dra, mag. 3.75), and Giausar (Lambda Dra, mag. 3.85).
Alrakis – Mu Draconis
| Spectral class | F7V |
| U-B colour index | −0.01 |
| B-V colour index | +0.47 |
| Apparent magnitude | 4.92 (5.66 / 5.69) |
| Absolute magnitude | +2.73 |
| Distance | 89 ± 1 light-years (27.4 ± 0.3 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 36.45 ± 0.46 mas/yr |
| Radial velocity | −17.30 ± 0.5 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: 58.16 ± 0.56 mas/yr |
| Dec.: 67.87 ± 0.56 mas/yr | |
| Mass (μ Dra A, μ Dra Ba, μ Dra Bb, μ Dra C) | 1.35 M☉, 1.30 M☉, 0.2 M☉, 0.29 M☉ |
| Metallicity (μ Dra A) | -0.01 dex |
| Age (μ Dra B) | 2.2 billion years |
| Constellation | Draco |
| Right ascension | 17h 05m 20.12403s |
| Declination | +54° 28′ 12.0994″ |
| Names and designations | Mu Draconis, μ Dra, 21 Draconis, HIP 83608, BD+54° 1857, SAO 30239, GC 23092, PPM 35805, AG+54 1079, GJ 9584, PLX 3890, UBV 14438, IRAS 17042+5432, 2MASS J17052018+5428126, CCDM J17053+5428AB, ADS 10345 AB, IDS 17033+5436 AB, WDS J17053+5428AB |
| Mu Draconis A | Alrakis, Mu Draconis A, μ Dra A, HD 154906, HR 6370, TYC 3890-1396-2, Gaia DR2 1420101696287738368, Gaia DR3 1420101696287738368 |
| Mu Draconis B | Mu Draconis , μ Dra B, HD 154905, HR 6369, GCRV 9877, TYC 3890-1396-1, Gaia DR2 1420101696285626624, Gaia DR3 1420101696285626624 |