Subra, Omicron Leonis (ο Leo), is a binary star located 133.53 light-years away in the constellation Leo. It has an apparent magnitude of 3.52. It appears close to Regulus in the sky and marks the right knee or paw of the celestial Lion.
Star system
Omicron Leonis is a spectroscopic binary star system composed of Omicron Leonis Aa and Omicron Leonis Ab. The system has an estimated age of 1.06 billion years.
The two components orbit each other with a period of 14.498068(6) at a separation of only 0.1834 ± 0.0007 astronomical units (AU), or 18.34% of the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. This is less than half Mercury’s orbital distance to the Sun. The two stars cannot be resolved even in the largest of telescopes. The presence of the fainter companion can only be deduced from the changes in the spectrum of the primary component.
The primary star, Omicron Leonis Aa, is a yellow giant star of the spectral type F8-G0III. It has a mass of 2.074 solar masses and a radius 5.73 times that of the Sun. With an effective temperature of 6,107 K, it is 41.1 times more luminous than the Sun.
The companion, Omicron Leonis Ab, is a main sequence star with the stellar classification A7m. It has a mass of 1.841 solar masses and a radius 2.43 times that of the Sun. It has an energy output of 17.8 Suns with a surface temperature of around 7,600 K.
The binary pair has an optical companion, Omicron Leonis B, a much fainter and more distant star with an apparent magnitude of 10.71. The visual companion is a little hotter and more massive than the Sun. Since its separation was first measured 350 years ago, the star has moved by about half an arcminute away from the Omicron Leonis A pair.
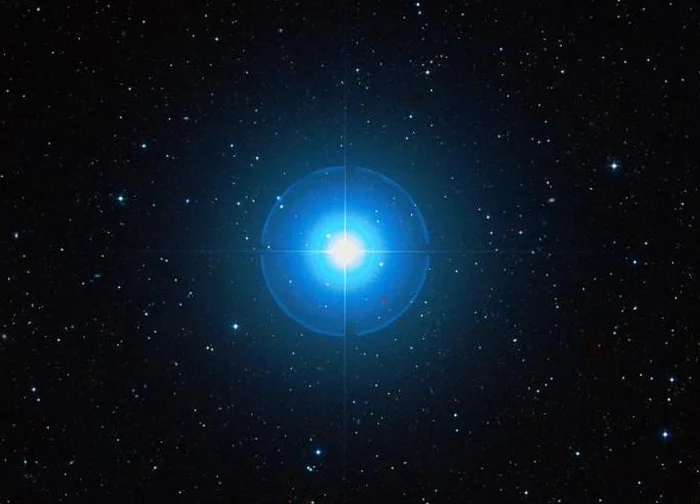

Subra (Omicron Leonis), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Facts
With an apparent magnitude of 3.52, Subra is the ninth brightest star in Leo, after Regulus, Algieba, Denebola, Zosma, Epsilon Leonis, Chertan, Adhafera, and Eta Leonis.
Subra is about as bright as Sadalbari (Mu Pegasi) in the constellation Pegasus, Rana (Delta Eridani) in Eridanus, Phi Velorum in Vela, and Xi2 Sagittarii in Sagittarius.
Omicron Leonis lies close to the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun and planets across the sky. The star can be occulted by the Moon and, much less frequently, by planets.
Subra was part of an Arabic lunar mansion called al-asad, the lion.
In Chinese astronomy, Subra formed the Xuanjuan asterism (軒轅,Xuānyuán) with 10 Ursae Majoris, HD 77912, 38 Lyncis, Alpha Lyncis, HIP 47617, f Leonis, Kappa Leonis, Alterf (Lambda Leonis), Epsilon Leonis, Rasalas (Mu Leonis), Adhafera (Zeta Leonis), Algieba (Gamma Leonis), Eta Leonis, Regulus (Alpha Leonis), Shaomin (Rho Leonis), and 31 Leonis. The asterism represented Xuanjuan, the Yellow Emperor.
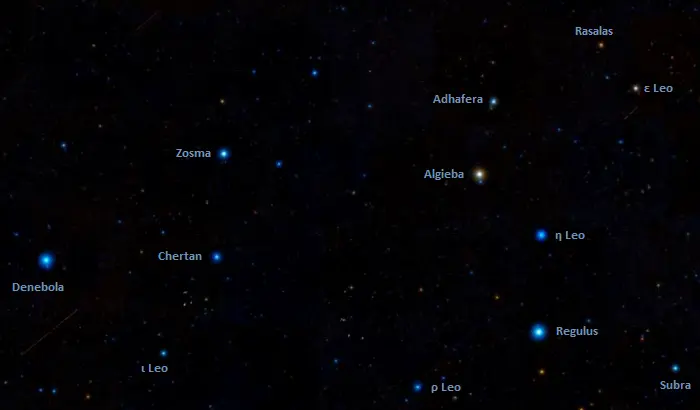

Leo stars, image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Name
The name Subra (pronunciation: /ˈsuːbrə/) comes from the Arabic zubra, denoting the mane, shoulder, or upper part of the back. The name originally applied to Zosma (Delta Leonis) and Chertan (Theta Leonis), the stars in the Lion’s hindquarters.
The name does not refer to the position of Omicron Leonis in the constellation figure of Leo. The star marks either the Lion’s right knee or one of its forepaws.
The International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) approved the name Subra on September 12, 2016. The name formally applies only to the primary component in the system, Omicron Leonis Aa.
Location
Subra is easy to find because it appears close to the bright Regulus in the sky. The star marks one of the celestial Lion’s forepaws and is the brightest point of light just west of Regulus, the star that marks the Lion’s heart. Regulus lies at the base of the Sickle, the asterism that outlines the Lion’s head and mane. The bright star can be found by extending a line from Megrez through Phecda in the Big Dipper across the sky.
At declination +09° 53’, Subra is close enough to the celestial equator to be visible from both hemispheres.
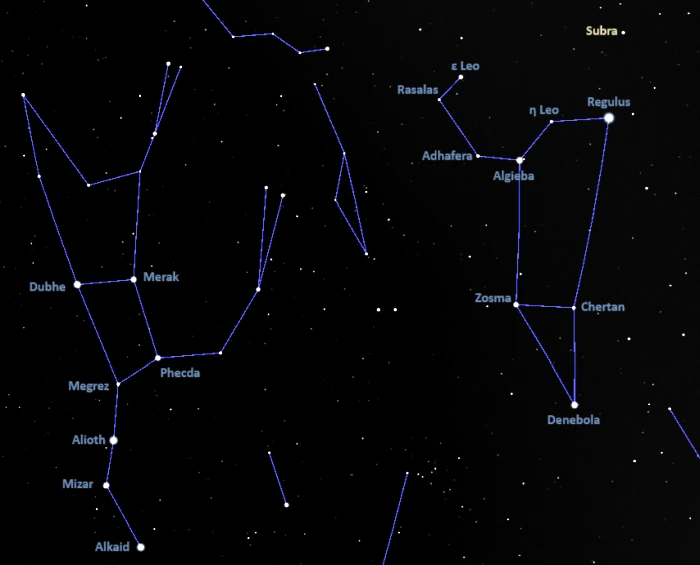
The location of Subra (Omicron Leonis), image: Stellarium
Constellation
Subra is located in the constellation Leo. The Lion is one of the ancient constellations listed by the astronomer Claudius Ptolemy in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. In Greek mythology, it represents the Nemean Lion, a mythical creature defeated by Heracles as part of his twelve labours.
Leo stretches across 947 square degrees of the predominantly northern sky close to the celestial equator. It is the 12th largest constellation in the sky. Like all equatorial constellations, it is easily visible from both the northern and southern hemispheres for at least part of the year.
Leo is also one of the constellations of the zodiac, which lie on the ecliptic, the Sun’s apparent path across the sky. When the Sun appears in Leo, from August 10 to September 16, the constellation is not visible at night.
Leo is home to Regulus, the 21st brightest star in the sky. The massive blue subgiant star shines at magnitude 1.40 from a distance of 79.3 light years. It is part of the Sickle of Leo, a relatively bright star pattern that forms the Lion’s head, mane and shoulders.
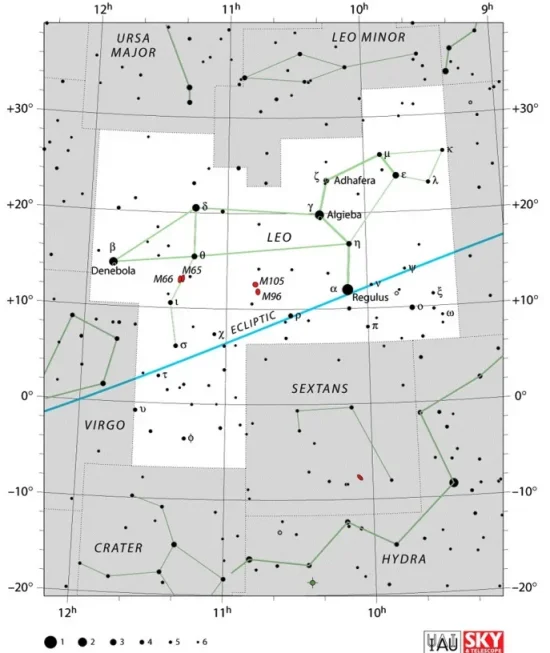
Leo constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Other notable stars in Leo include the carbon star CW Leonis, the red dwarf Wolf 359, the fifth nearest individual star to the Sun (after Proxima Centauri, Toliman, Rigil Kentaurus and Barnard’s Star), the blue supergiant Icarus (MACS J1149 Lensed Star 1), one of the most distant stars known, and Caffau’s Star (SDSS J102915+172927), one of the oldest stars known in the Milky Way.
Leo also hosts the A-type main sequence stars Denebola (Beta Leonis), Chertan (Theta Leonis) and Zosma (Delta Leonis), the variable binary star Gamma Leonis (Algieba), composed of two giants, the yellow bright giant Epsilon Leonis, the F-type giant Adhafera (Zeta Leonis), the red giant Pi Leonis, the orange giants Alterf (Lambda Leonis) and Kappa Leonis, the blue-white supergiant Eta Leonis, the blue supergiant Shaomin (Rho Leonis), and the chemically peculiar orange giant Rasalas (Mu Leonis), which hosts an orbiting exoplanet.
Leo contains two bright galaxy groups, the Leo Triplet (Messier 65, Messier 66 and NGC 3628) and the Leo I Group (Messier 95, Messier 96 and Messier 105). Both groups lie in the region between Regulus and Denebola.
Other deep sky objects in the constellation include the Frosty Leo Nebula, the Owl Galaxy (NGC 3758), and the Cosmic Horseshoe, a gravitationally lensed system of two distant galaxies discovered in 2007.
The best time of the year to see the stars and deep sky objects in Leo is during the month of April, when the constellation is higher above the horizon in the early evening.
The 10 brightest stars in Leo are Regulus (Alpha Leo, mag. 1.40), Algieba (Gamma Leo, mag. 2.08), Denebola (Beta Leo, mag. 2.113), Zosma (Delta Leo, mag. 2.56), Epsilon Leonis (mag. 2.98), Chertan (Theta Leo, mag. 3.324), Adhafera (Zeta Leo, mag. 3.33), Eta Leonis (mag. 3.486), Subra (Omicron Leo, mag. 3.52), and Shaomin (Rho Leo, mag. 3.9).
Subra – Omicron Leonis
| Spectral class | F8-G0III + A7m |
| U-B colour index | +0.21 |
| B-V colour index | +0.49 |
| Apparent magnitude | 3.52 |
| Absolute magnitude | 0.51 |
| Distance | 133.53 ± 0.45 light-years (40.96 ± 0.14 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 24.412 ± 0.081 mas |
| Radial velocity | 26.18 ± 0.05 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: -142.621 ± 0.262 mas/yr |
| Dec.: -37.338 ± 0.184 mas/yr | |
| Constellation | Leo |
| Right ascension | 09h 41m 09.0321741326s |
| Declination | 09° 53′ 32.308426423″ |
| Names and designations | Subra, Omicron Leonis, ο Leonis, ο Leo, 14 Leonis, 14 Leo, HD 83808/HD 83809, HR 3852, HIP 47508, SAO 98709, FK5 365, PPM 156093, BD+10 2044, AG+10 1245, GC 13366, GCRV 6240, PLX 2299.00, SKY# 18720, CSI+10 2044 1, GEN# +1.00083808, GSC 00821-02130, JP11 1844, N30 2313, HMM 1, ARI 1, IRC +10210, PMC 90-93 261, Renson 23896, ROT 1500, SBC7 386, IRAS 09384+1007, 2MASS J09410902+0953321, SRS 30365, UBV 9195, UBV M 15636, WEB 8912, RX J0941.1+0953 1, RX J0941.1+0953, 1RXS J094110.2+095330, YZ 10 3836, TD1 14176, TIC 469018187, TYC 821-2130-1, Gaia DR2 588551497558573056, Gaia DR3 588551501854159744, ADS 7480 A, CCDM J09412+0954A, IDS 09358+1021 A, PMSC 09358+1020, PMSC 09358+1020Aab, PMSC 09358+1020Aac, WDS J09412+0954Aa,Ab, WDS J09412+0954A, WDS J09412+0954Aa,Ac |
Omicron Leonis Aa
| Mass | 2.074 ± 0.013 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 41.1 L☉ (36 – 46.9 L☉) |
| Radius | 5.73 ± 0.34 R☉ |
| Temperature | 6,107 ± 93 K |
| Metallicity | 0.11 ± 0.10 dex |
| Age | 1.06 ± 0.03 billion years |
Omicron Leonis Ab
| Mass | 1.841 ± 0.011 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 17.8 L☉ (13.5 – 23.5 L☉) |
| Radius | 2.43 ± 0.35 R☉ |
| Temperature | 7,600 ± 200 K |
| Metallicity | 0.11 ± 0.10 dex |
| Age | 1.06 ± 0.03 billion years |