Tabit, Pi3 Orionis (π3 Ori) is an F-type main sequence star located 26.32 light-years away in the constellation Orion. With an apparent magnitude of 3.16, it is visible to the unaided eye. The star forms Orion’s Shield (or Orion’s Bow) with five other stars and star systems that share the Bayer designation Pi Orionis.
Star type
Tabit is a yellow-white main sequence star of the spectral type F6 V. It has a mass of 1.288 solar masses and a radius 1.317 times that of the Sun. With a surface temperature of 6,518 K, it is 2.816 times more luminous than the Sun. The star spins at 17 km/s. It has an estimated age of 104 billion years.
Pi3 Orionis is believed to be a single star. It has a visual companion, a magnitude 8.8 star, and is listed as CCDM J04499+0657A in the Catalog of Components of Double & Multiple Stars. The Washington Visual Double Star Catalog lists other companions, also likely optical.
Even though researchers reported detecting a periodicity of 73.26 days, this is believed to be linked with stellar activity and not to the presence of a planet. No planets have been detected orbiting the star to date.
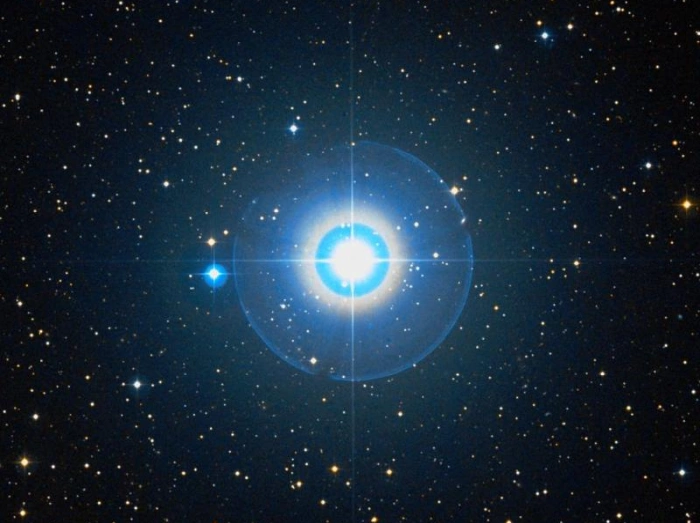

Tabit (Pi³ Orionis), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Facts
Tabit is the ninth brightest star in Orion, after Rigel (Beta Orionis), Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis), Bellatrix (Gamma Orionis), Alnilam (Epsilon Orionis), Alnitak (Zeta Orionis), Saiph (Kappa Orionis), Mintaka (Delta Orionis), and Hatysa (Iota Orionis). On average, Pi3 Orionis is the 207th brightest star in the sky. It is about as bright as Haedus (Eta Aurigae), Epsilon Leporis, and Xami (Alpha Circini).
Tabit has served as a spectral standard for its class (F6 V) since 1943. The star’s spectrum is one of the stable anchor points used to classify other stars.
Tabit (Pi3 Orionis) shares the Bayer designation Pi Orionis with five unrelated stars and star systems: Pi1 Orionis, Pi2 Orionis, Pi4 Orionis, Pi5 Orionis, and Pi6 Orionis. Tabit is the brightest and nearest of the five stars. It is also the only one that has a proper name.
Pi1 and Pi2 Orionis are A-type main sequence stars located 116 and 224 light-years away, Pi4 and Pi5 Orionis are hot blue B-type giants located 1,050 and 1,300 light-years away, and Pi6 Orionis is an orange giant located 950 light-years away. Pi4 and Pi5 Orionis are binary stars, while others are believed to be solitary.
The six stars and star systems form Orion’s Shield (or Orion’s Bow), one of three prominent asterisms in the constellation Orion, along with the brighter Orion’s Belt and Orion’s Sword. In depictions of the Hunter constellation, the stars that share the Bayer designation Pi Orionis represent either Orion’s shield, Orion’s bow, or the lion’s hide held by the mythical hunter. Pi1 Orionis lies almost 9 degrees north of Pi6 Orionis.
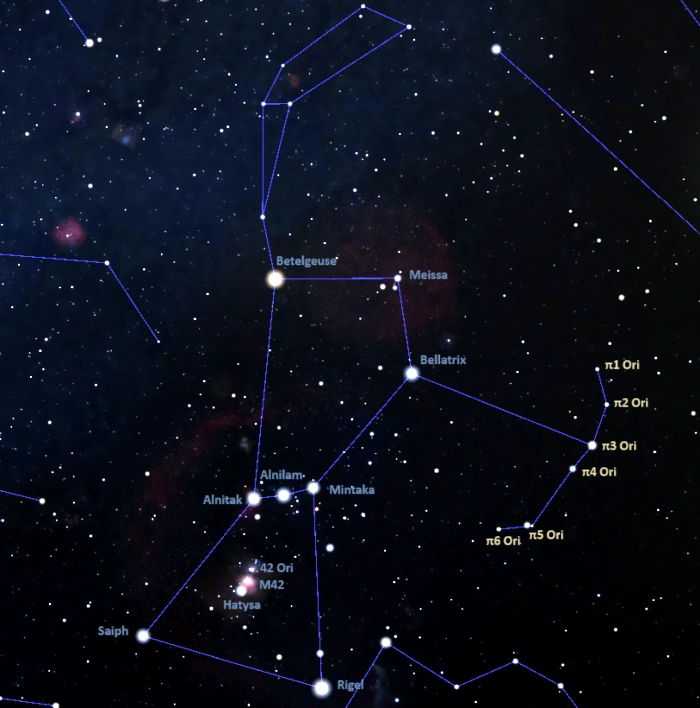
Orion’s Shield, image: Stellarium
In Persian astronomy, the stars of Orion’s Shield were known as Al Taj (“the crown” or “the tiara”). In Arabic astronomy, they were called Al Kumm (“the sleeve”) and Al Dhawain (“anything pendent”).
The 10th century Persian astronomer Al Sufi called the stars Manica, referring to a sleeve in heraldry.
Name
The name Tabit (pronunciation: /ˈteɪbɪt/) comes from the Arabic al-thābit, meaning “the endurer” or “the fixed one (the constant one).” The name was approved by the International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) on September 5, 2017.
Pi3 Orionis traditionally shared the name Tabit (or Thabit) with the fainter Upsilon Orionis, a hot blue star in the region of Orion’s Sword.
In traditional Chinese astronomy, Tabit was known as 參旗六 (Zhāng Qí Liù), the Sixth Star of Banner of Three Stars. It formed the Banner of Three Stars asterism with Omicron1 Orionis, Omicron2 Orionis, 6 Orionis, Pi1 Orionis, Pi2 Orionis, Pi4 Orionis, Pi5 Orionis, and Pi6 Orionis. The asterism was part of the larger Net mansion, which represented the body of the White Tiger.
Location
Tabit is very easy to find because it is part of Orion’s Shield, a relatively bright star pattern that lies west of the main constellation figure of the Hunter. Tabit is the brightest and westernmost of the Shield stars. It appears roughly two-thirds of the way from Rigel in Orion to Aldebaran in Taurus.
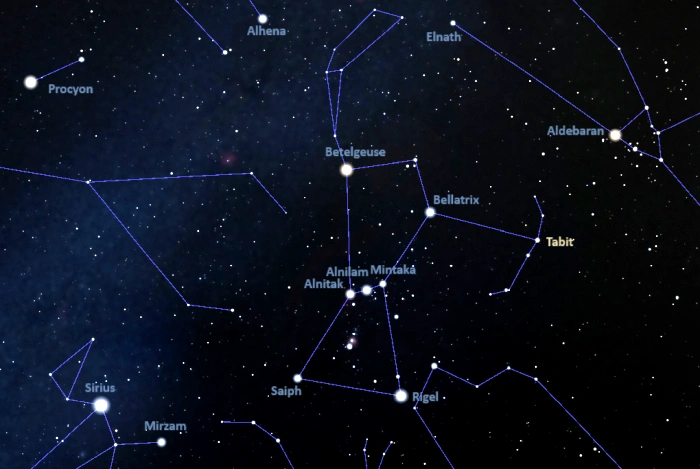
The location of Tabit (Pi³ Orionis), image: Stellarium
Constellation
Tabit is located in the constellation Orion. The celestial Hunter is one of the brightest and best-known constellations in the night sky. It is the 26th largest of the 88 constellations, stretching across 594 square degrees of the sky on the celestial equator. Like all equatorial constellations, it is easily visible from both the northern and southern hemisphere.
Orion is one of the 48 ancient constellations catalogued by the Greco-Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. The constellation is associated with the giant huntsman Orion in Greek mythology. The mythical hunter was known for his exceptional strength and skill.
Orion is best-known for being home to the supergiants Rigel and Betelgeuse, the seventh and 10th brightest stars in the sky, and for containing the Orion Nebula (Messier 42), the nearest massive stellar nursery to the solar system. The constellation also hosts Orion’s Belt, one of the most recognizable asterisms in the sky.
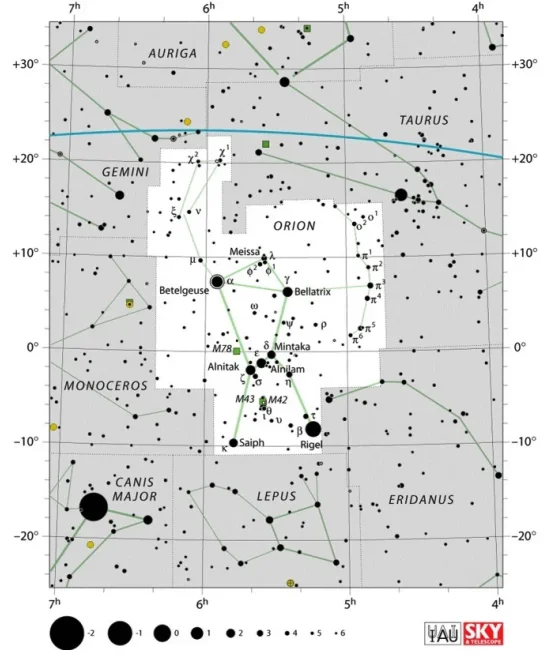
Orion constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Other notable stars in Orion include the hot blue star Bellatrix, the blue giants Meissa and Hatysa, the blue supergiants Saiph, Alnilam and Alnitak, and the bright giant Mintaka.
The best-known deep sky objects in the constellation include the Orion Nebula (Messier 42) with the Trapezium Cluster, De Mairan’s Nebula (Messier 43), the emission nebulae NGC 2024 (the Flame Nebula), NGC 2174 (the Monkey Head Nebula), and Barnard’s Loop, the dark Horsehead Nebula (Barnard 33), the reflection nebulae Messier 78 and the Running Man Nebula (NGC 1977), and the open cluster NGC 2169 (the 37 Cluster).
The best time of the year to see the stars and deep sky objects in Orion is during the month of January, when the constellation climbs higher in the sky in the early evening. The entire constellation can be seen from locations between the latitudes 85° N and 75° S.
The 10 brightest stars in Orion are Rigel (Beta Ori, mag. 0.05 – 0.18), Betelgeuse (Alpha Ori, mag. 0.0 – 1.3), Bellatrix (Gamma Ori, mag. 1.59 to 1.64), Alnilam (Epsilon Ori, mag. 1.64 – 1.74), Alnitak A (Zeta Ori A, mag. 2.00), Saiph (Kappa Ori, mag. 2.09), Mintaka AB (Delta Ori AB, mag. 2.23), Hatysa (Iota Ori, mag. 2.77), Tabit (Pi3 Ori, mag. 3.16), and Eta Orionis (mag. 3.31 – 3.6).
Tabit – Pi3 Orionis
| Spectral class | F6 V |
| Variable type | Suspected |
| U-B colour index | +0.00 |
| B-V colour index | +0.46 |
| Apparent magnitude | 3.16 |
| Absolute magnitude | 3.65 |
| Distance | 26.32 ± 0.04 light-years (8.07 ± 0.01 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 124.6198 ± 0.2246 mas |
| Radial velocity | 22.47 ± 0.52 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: 463.954 ± 0.237 mas/yr |
| Dec.: 11.937 ± 0.181 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 1.288 ± 0.019 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 2.816 ± 0.06 L☉ |
| Radius | 1.317 ± 0.004 R☉ |
| Temperature | 6,518 ± 35 K |
| Metallicity | 0.03 ± 0.03 dex |
| Age | 1.04 billion years |
| Rotational velocity | 17 km/s |
| Surface gravity | 4.31 ± 0.01 cgs |
| Constellation | Orion |
| Right ascension | 04h 49m 50.4112051485s |
| Declination | +06° 57′ 40.600622266″ |
| Names and designations | Tabit, Pi3 Orionis, π3 Orionis, π3 Ori, 1 Orionis, HD 30652, HR 1543, HIP 22449, Gliese 178, SAO 112106, FK5 1134, BD+06°762, LTT 11517, NLTT 14011, PPM 148020, GC 5875, GCRV 2837, GCTP 1077.00, PLX 1077.00, Ci 20 306, CNS5 1208, CSI+06 762 1, CSV 100411, PMC 90-93 758, 1ES 0447+06.8, NSV 1731, SRS 31134, Zkh 65, EUVE J0449+06.9, 2EUVE J0449+06.9, LSPM J0449+0657, TD1 3592, GEN# +1.00030652, IRC +10071, N30 1028, RAVE J044950.4+065741, TIC 399665349, ROT 683, SKY# 7512, SPOCS 230, USNO-B1.0 0969-00046662, USNO 809, SV* ZI 311, uvby98 100030652, RE J0449+065, RE J044950+065733, 2RE J044951+065736, 2RE J0449+065, 1RXS J044950.6+065736, WEB 4331, IRAS 04471+0652, UBV 4635, UBV M 10360, 2MASS J04495040+0657409, TYC 96-1462-1, Gaia DR2 3288921720024442496, Gaia DR3 3288921720025503360, CCDM J04499+0657A, IDS 04444+0647 A, WDS J04498+0658A |